It is called turbomachinery to transfer the energy to the continuous flow of fluid by the dynamic action of the blades on the rotating impeller or to promote the rotation of the blades by the energy from the fluid. In turbomachinery, rotating blades do positive or negative work on a fluid, raising or lowering its pressure. Turbomachinery is divided into two main categories: one is the working machine from which the fluid absorbs power to increase the pressure head or water head, such as vane pumps and ventilators; The other is the prime mover, in which the fluid expands, reduces the pressure, or the water head produces power, such as steam turbines and water turbines. The prime mover is called the turbine, and the working machine is called the blade fluid machine.
According to the different working principles of the fan, it can be divided into blade type and volume type, among which blade type can be divided into axial flow, centrifugal type and mixed flow. According to the pressure of the fan, it can be divided into blower, compressor and ventilator. Our current mechanical industry standard JB/T2977-92 stipulates: The fan refers to the fan whose entrance is the standard air entrance condition, whose exit pressure (gauge pressure) is less than 0.015MPa; The outlet pressure (gauge pressure) between 0.015MPa and 0.2MPa is called the blower; The outlet pressure (gauge pressure) greater than 0.2MPa is called a compressor.
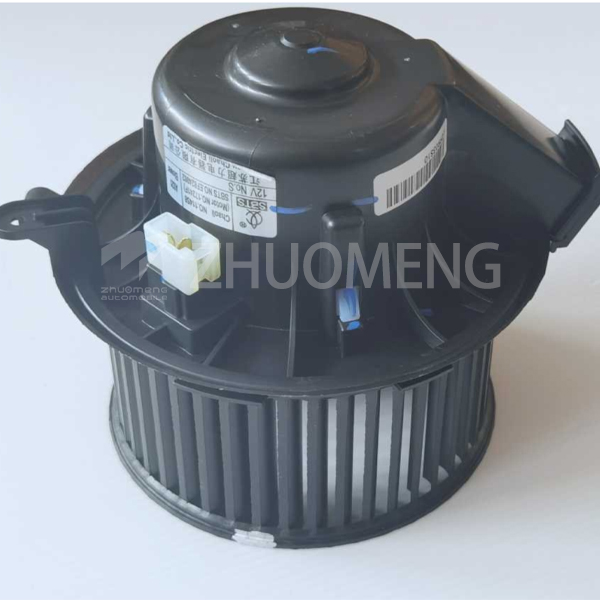
The main parts of the blower are: volute, collector and impeller.
The collector can direct the gas to the impeller, and the inlet flow condition of the impeller is guaranteed by the geometry of the collector. There are many kinds of collector shapes, mainly: barrel, cone, cone, arc, arc arc, arc cone and so on.
Impeller generally has wheel cover, wheel, blade, shaft disk four components, its structure is mainly welded and riveted connection. According to the impeller outlet of different installation angles, can be divided into radial, forward and backward three. The impeller is the most important part of the centrifugal fan, driven by the prime mover, is the heart of the centrifugal turinachinery, responsible for the energy transmission process described by the Euler equation. The flow inside the centrifugal impeller is affected by the impeller rotation and surface curvature and accompanied by deflow, return and secondary flow phenomena, so that the flow in the impeller becomes very complicated. The flow condition in the impeller directly affects the aerodynamic performance and efficiency of the whole stage and even the whole machine.
The volute is mainly used to collect the gas coming out of the impeller. At the same time, the kinetic energy of the gas can be converted into the static pressure energy of the gas by moderately reducing the gas speed, and the gas can be guided to leave the volute outlet. As a fluid turbomachinery, it is a very effective method to improve the performance and working efficiency of blower by studying its internal flow field. In order to understand the real flow condition inside centrifugal blower and improve the design of impeller and volute to improve the performance and efficiency, scholars have done a lot of basic theoretical analysis, experimental research and numerical simulation of centrifugal impeller and volute