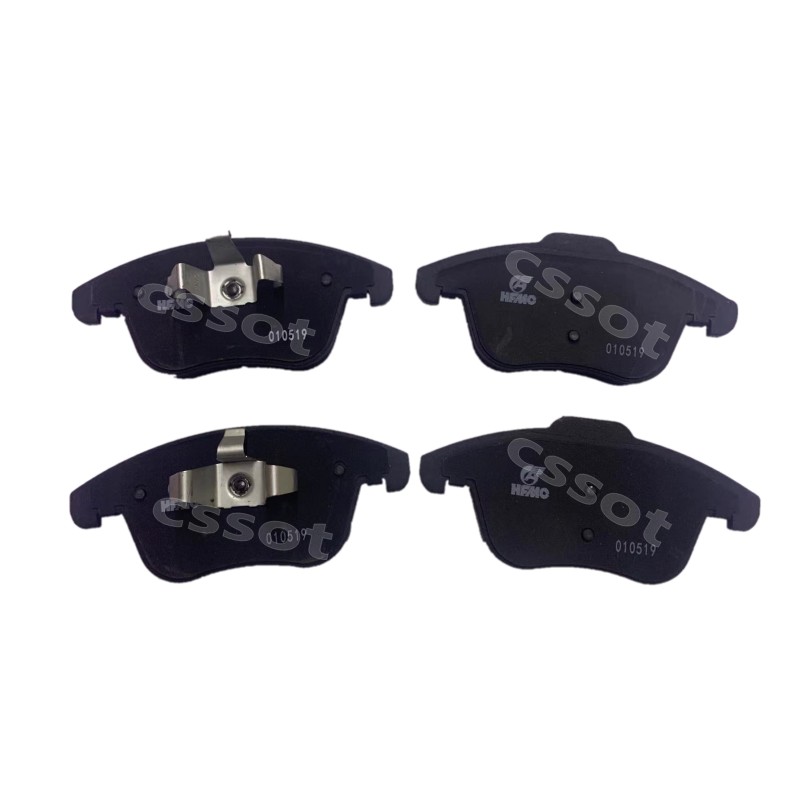
Newly Arrival Mg Zx Accessories Wholesale - SAIC MAXUS V80 Oil radiator – iron water pipe – VI Maxus wholesale supplier – Zhuomeng
Newly Arrival Mg Zx Accessories Wholesale - SAIC MAXUS V80 Oil radiator – iron water pipe – VI Maxus wholesale supplier – Zhuomeng Detail:
Products information
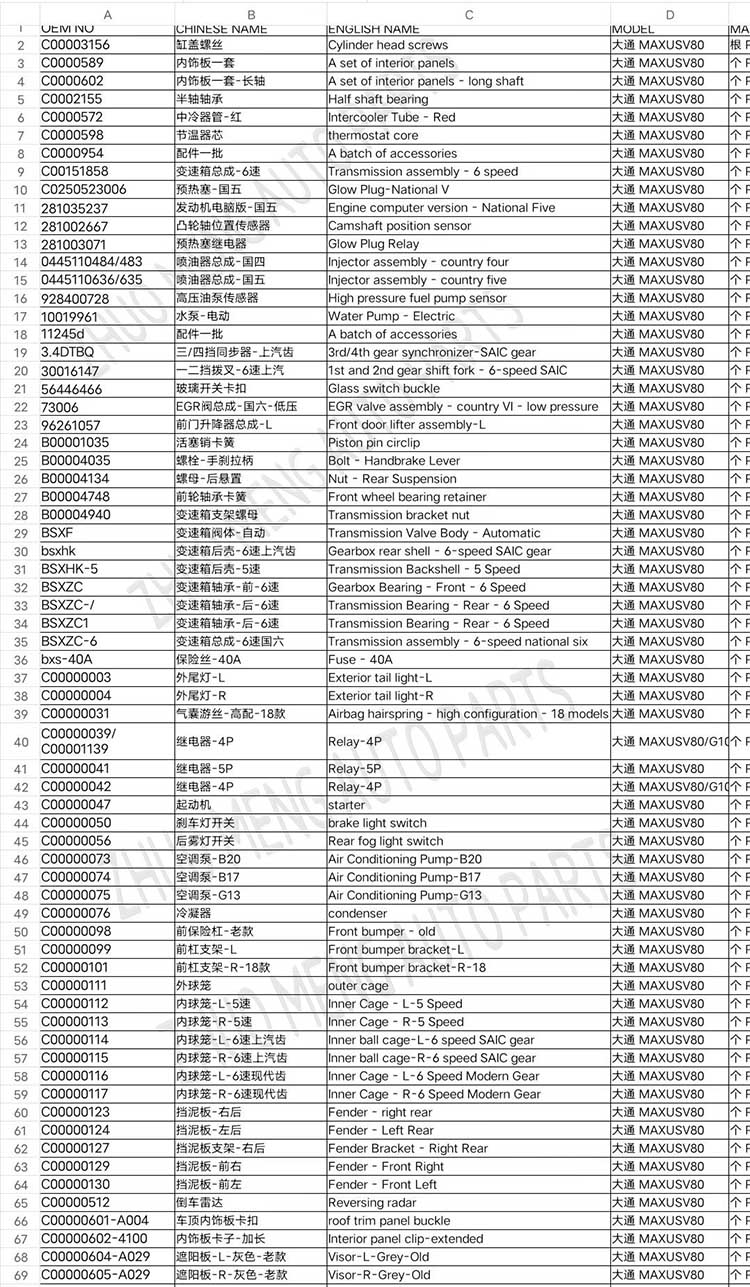
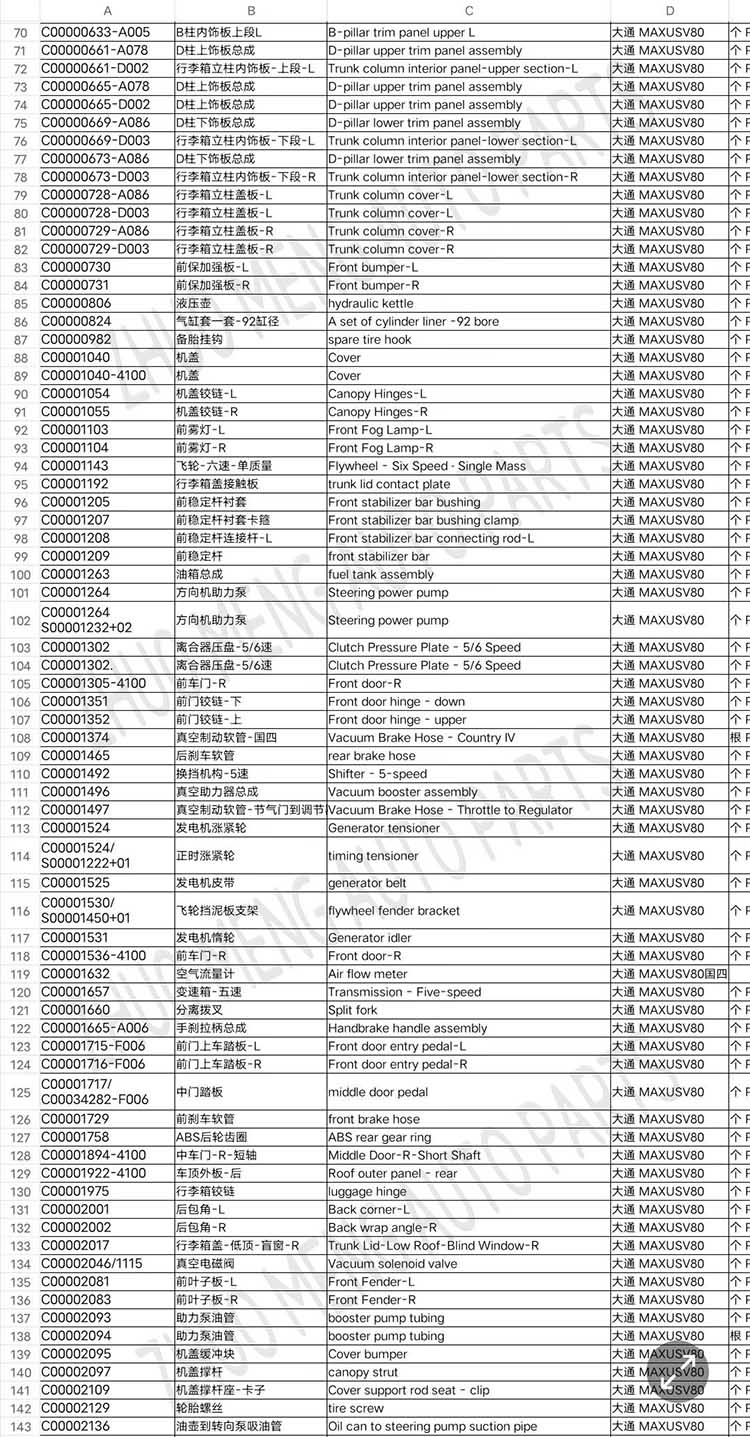
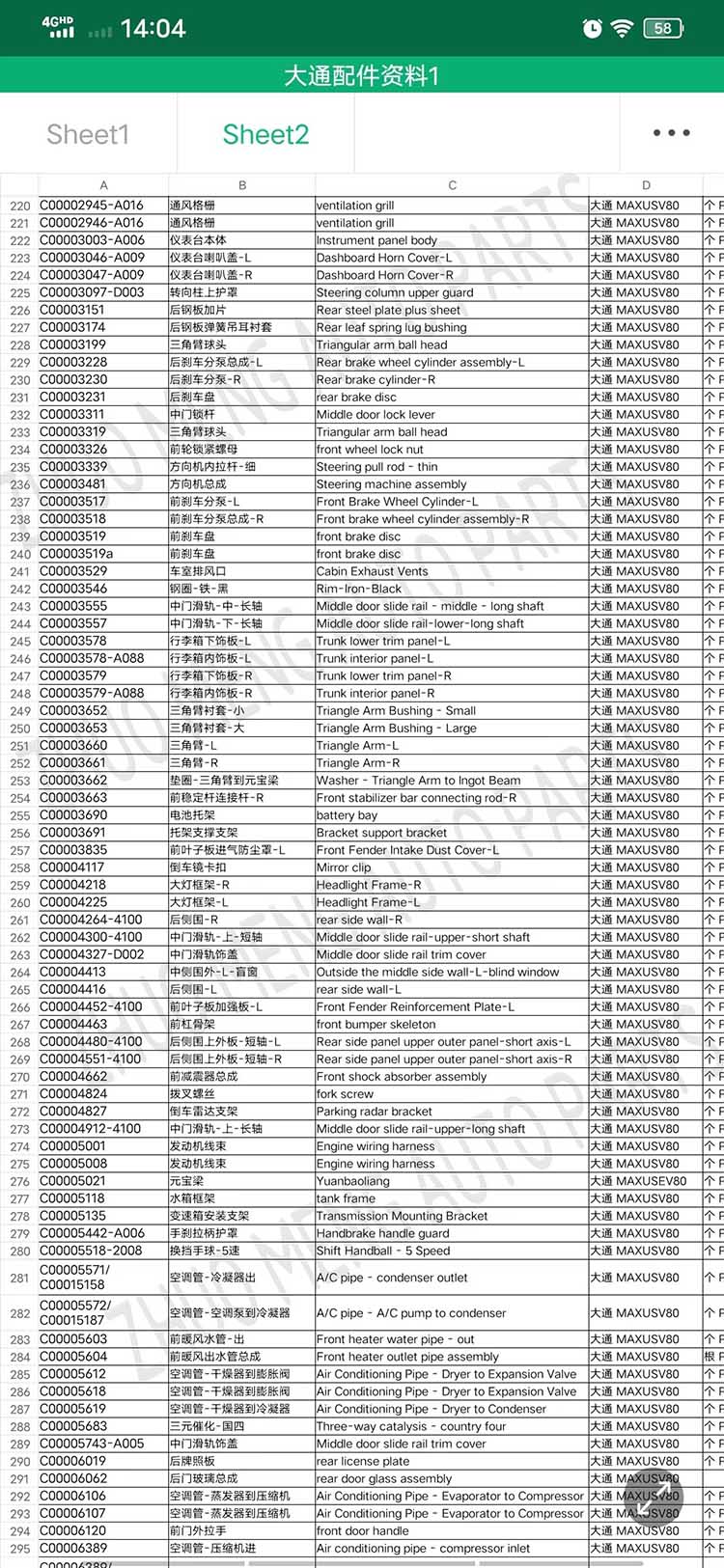
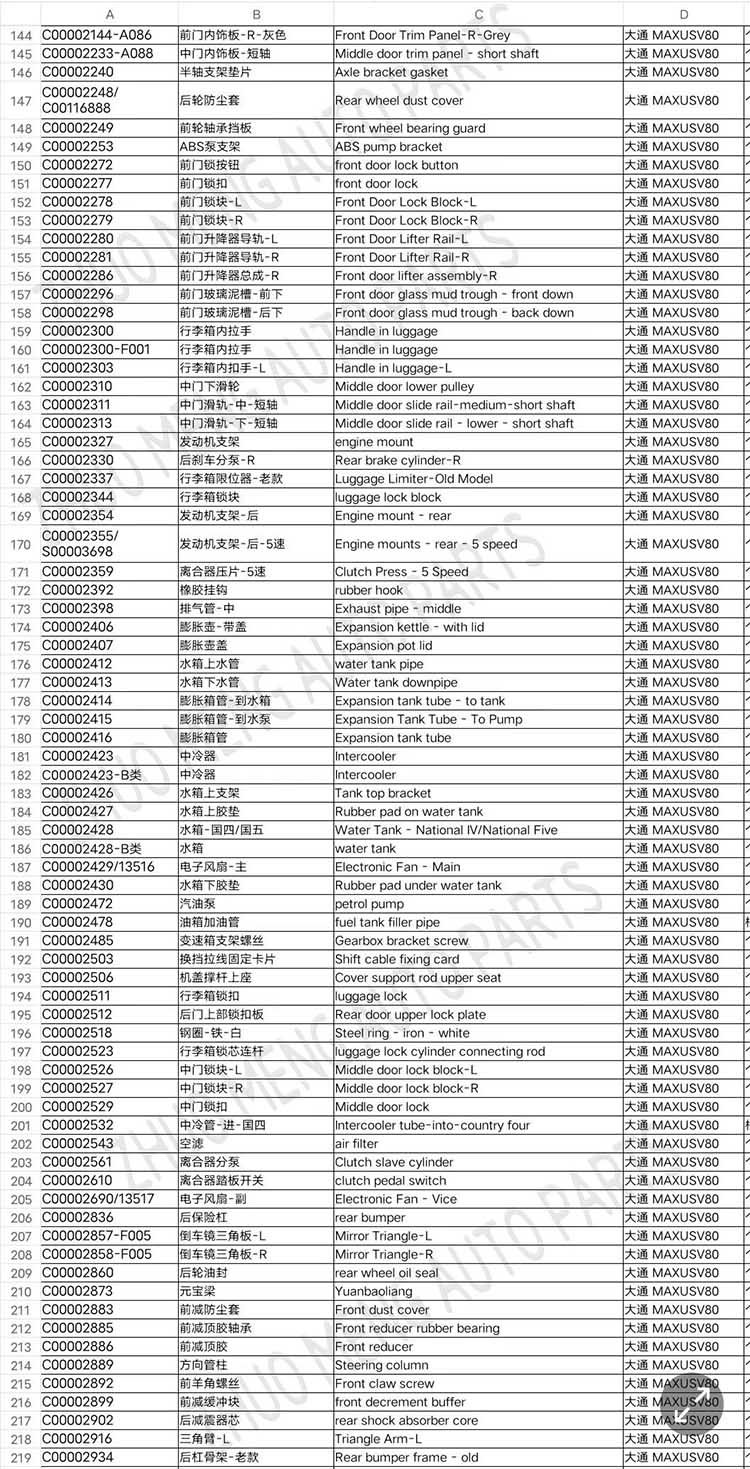
| Products name | Oil radiator |
| Products application | SAIC MAXUS V80 |
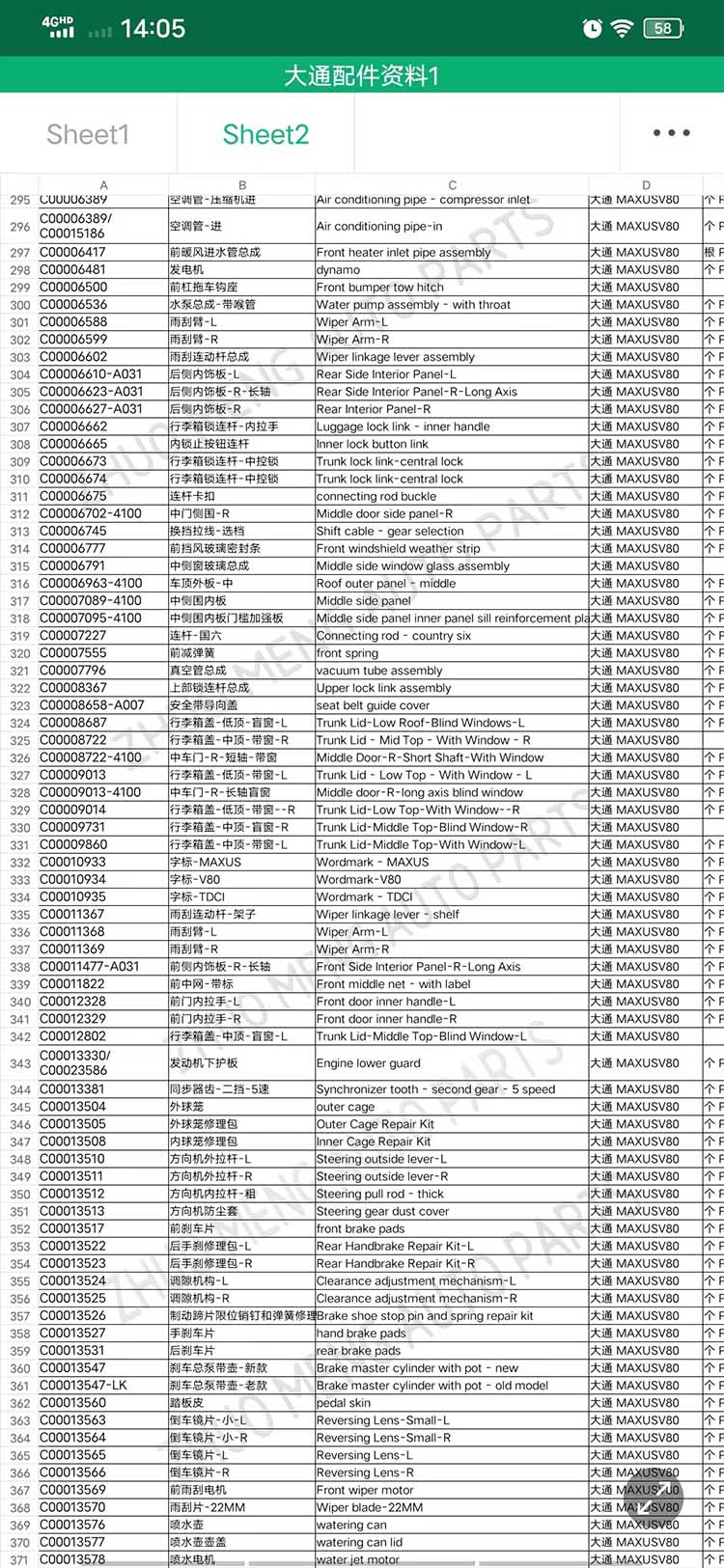
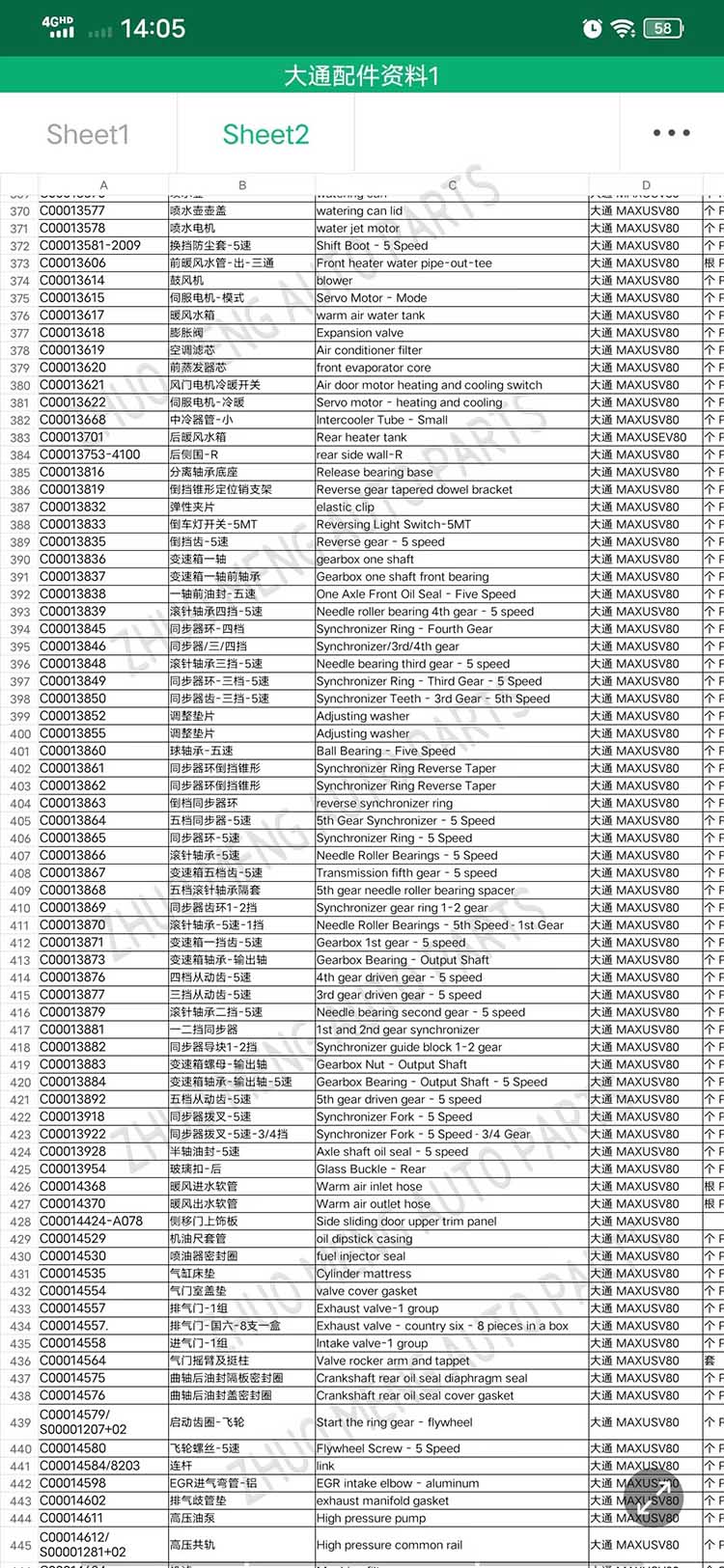
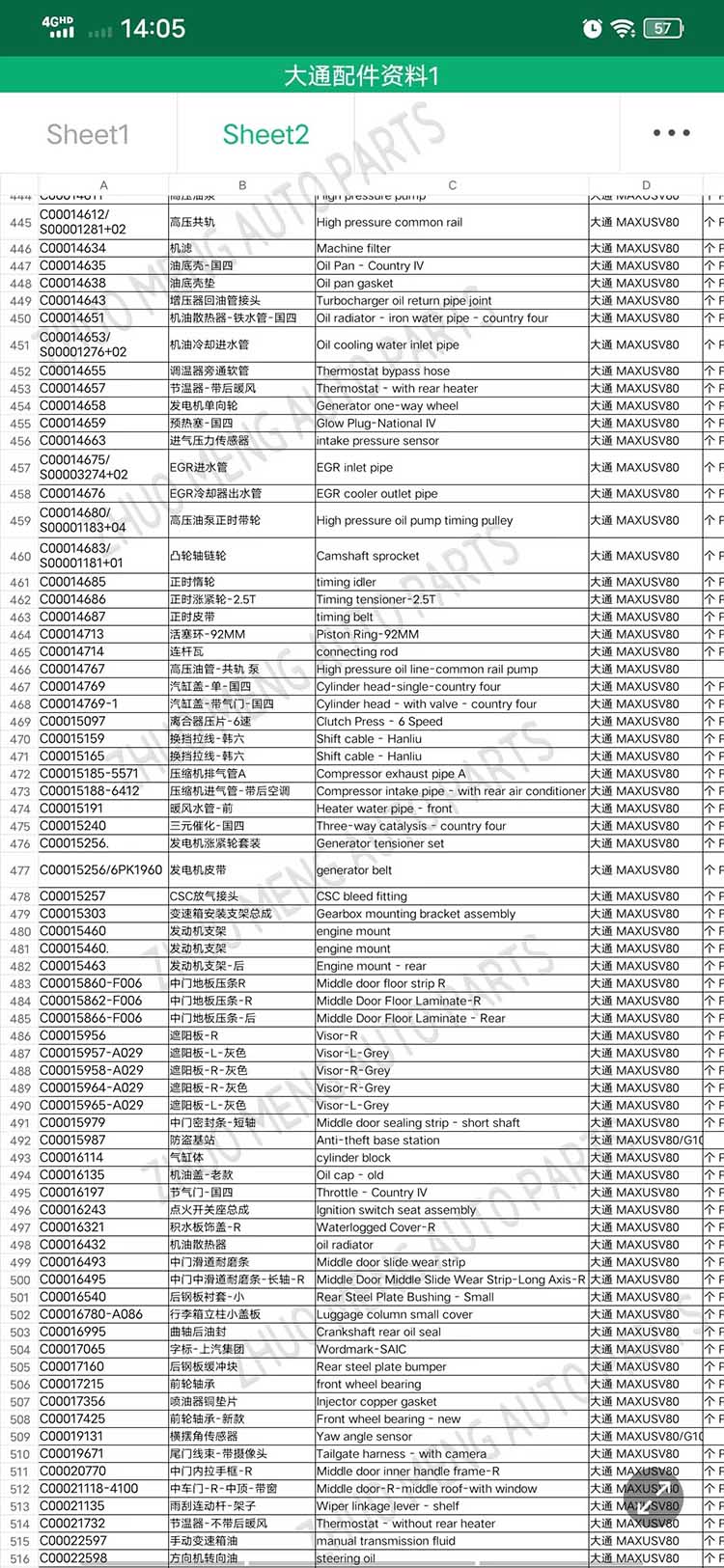
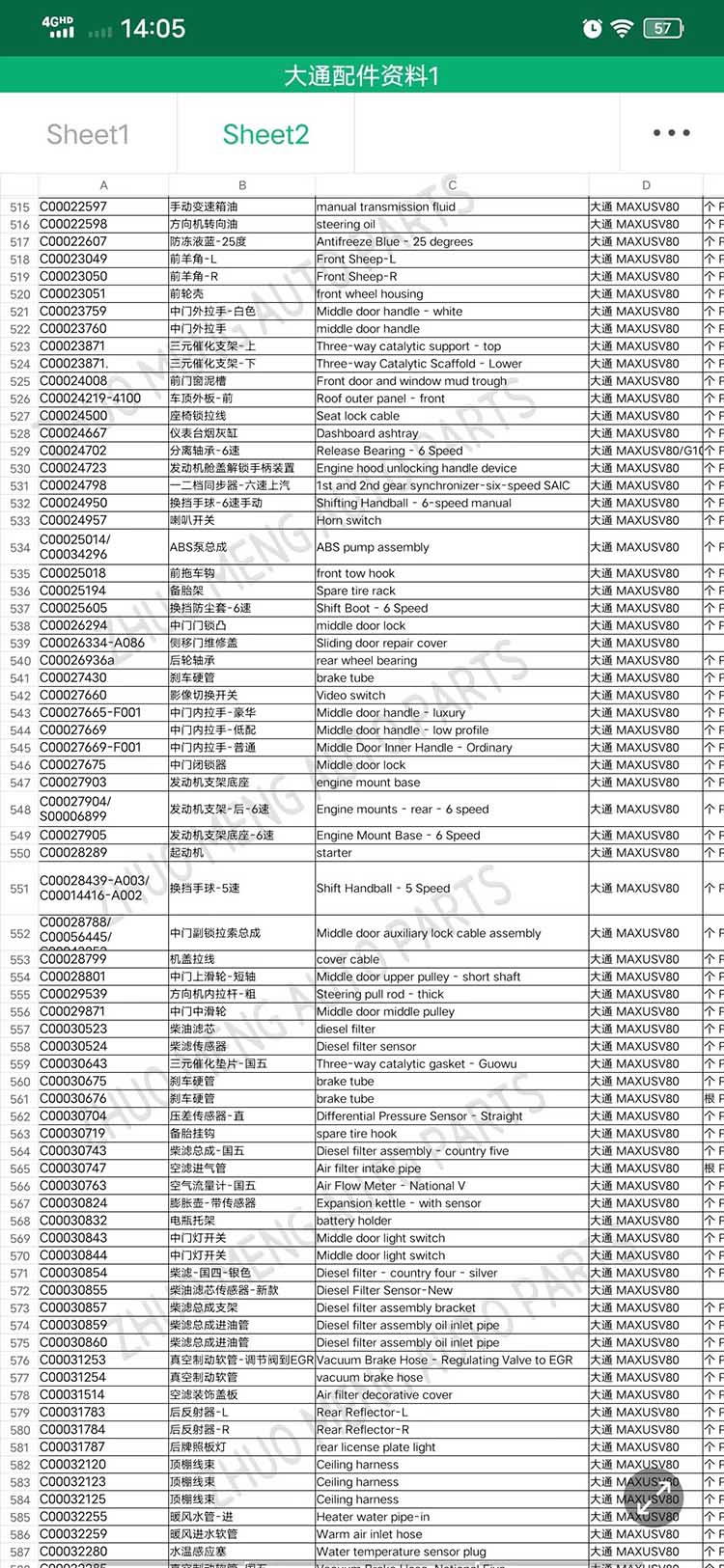
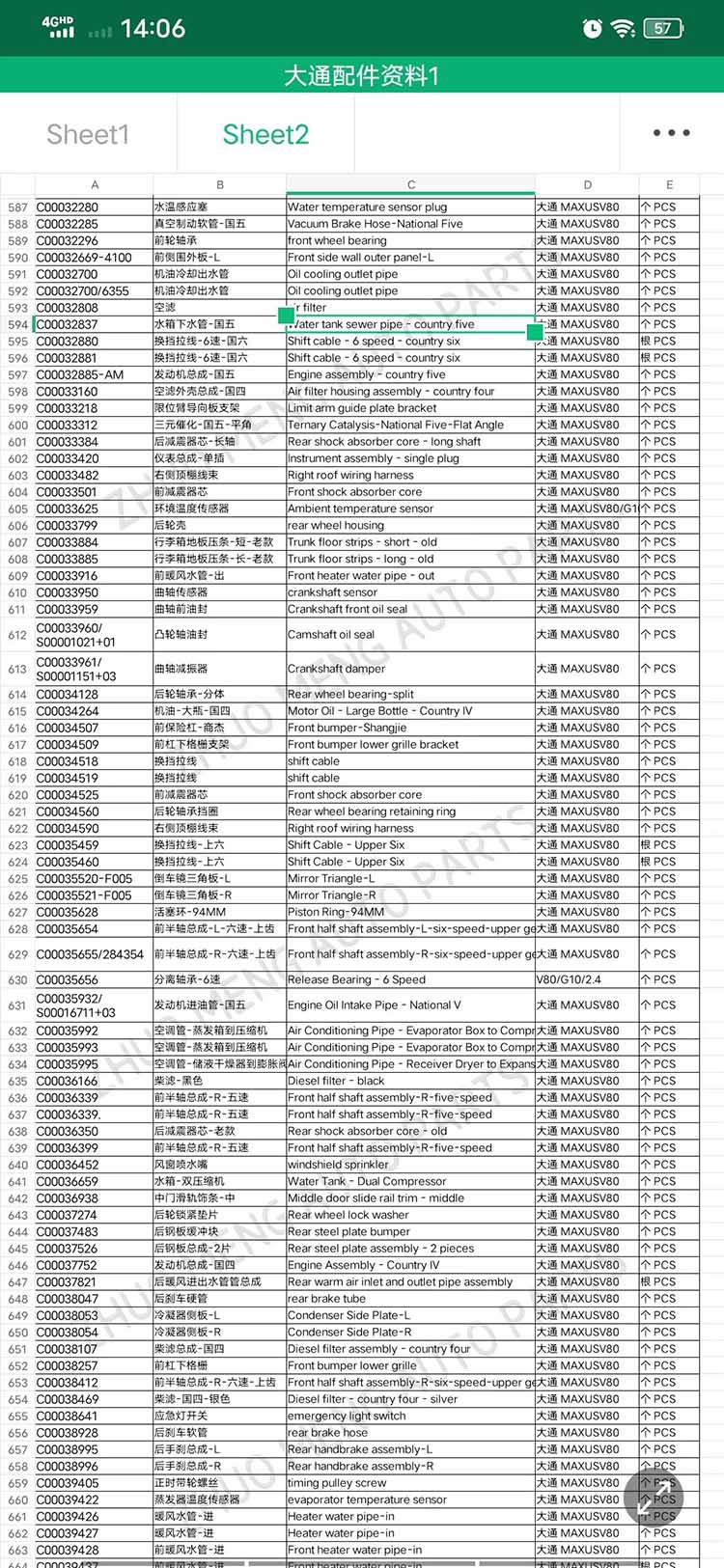
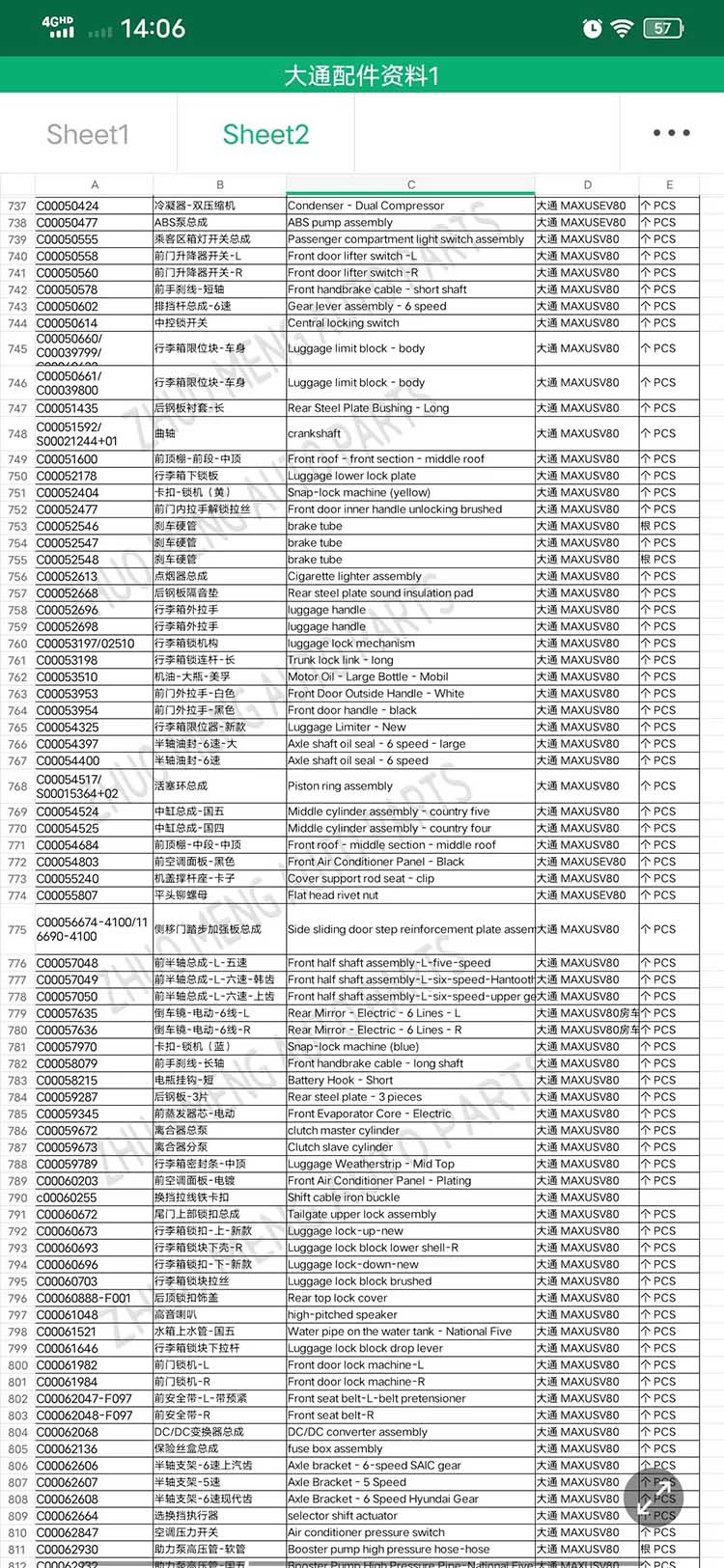
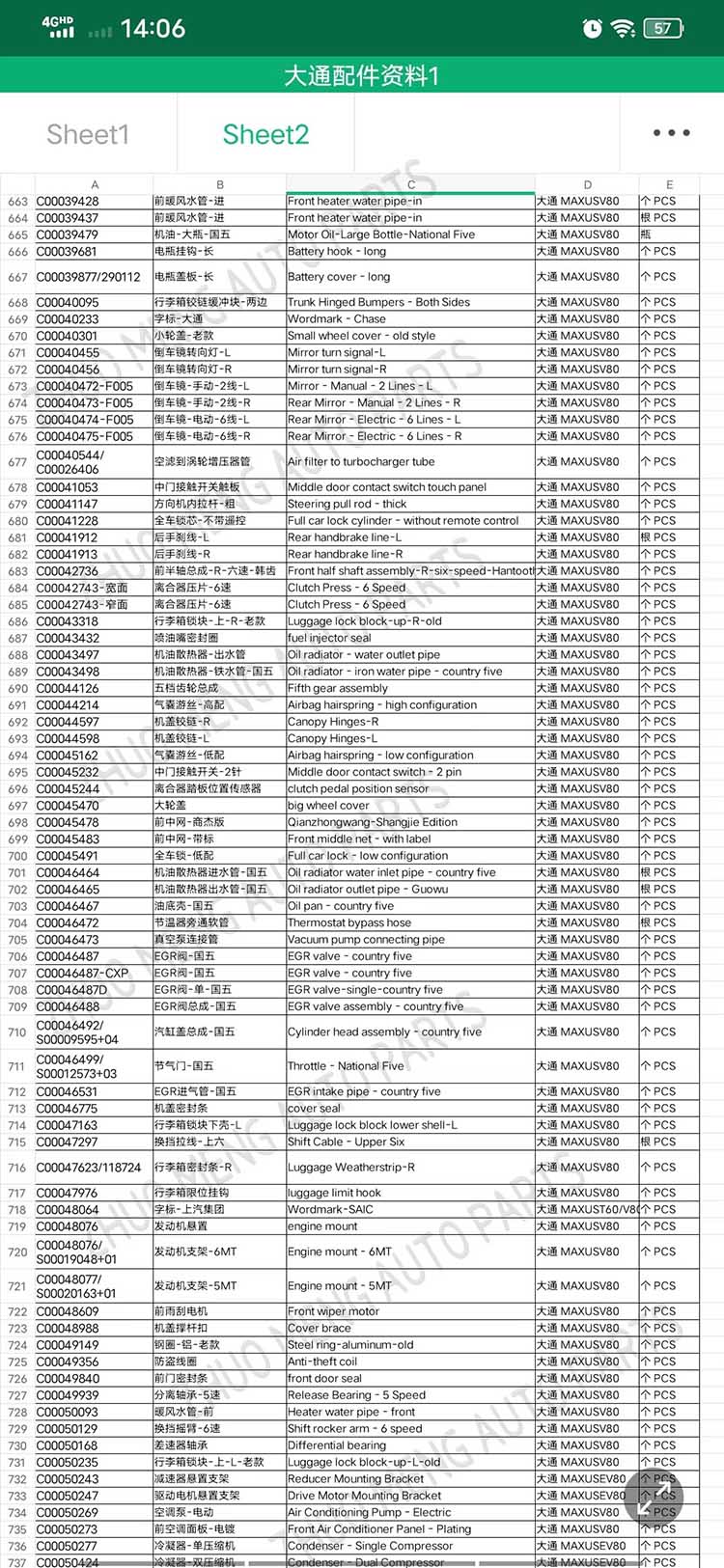
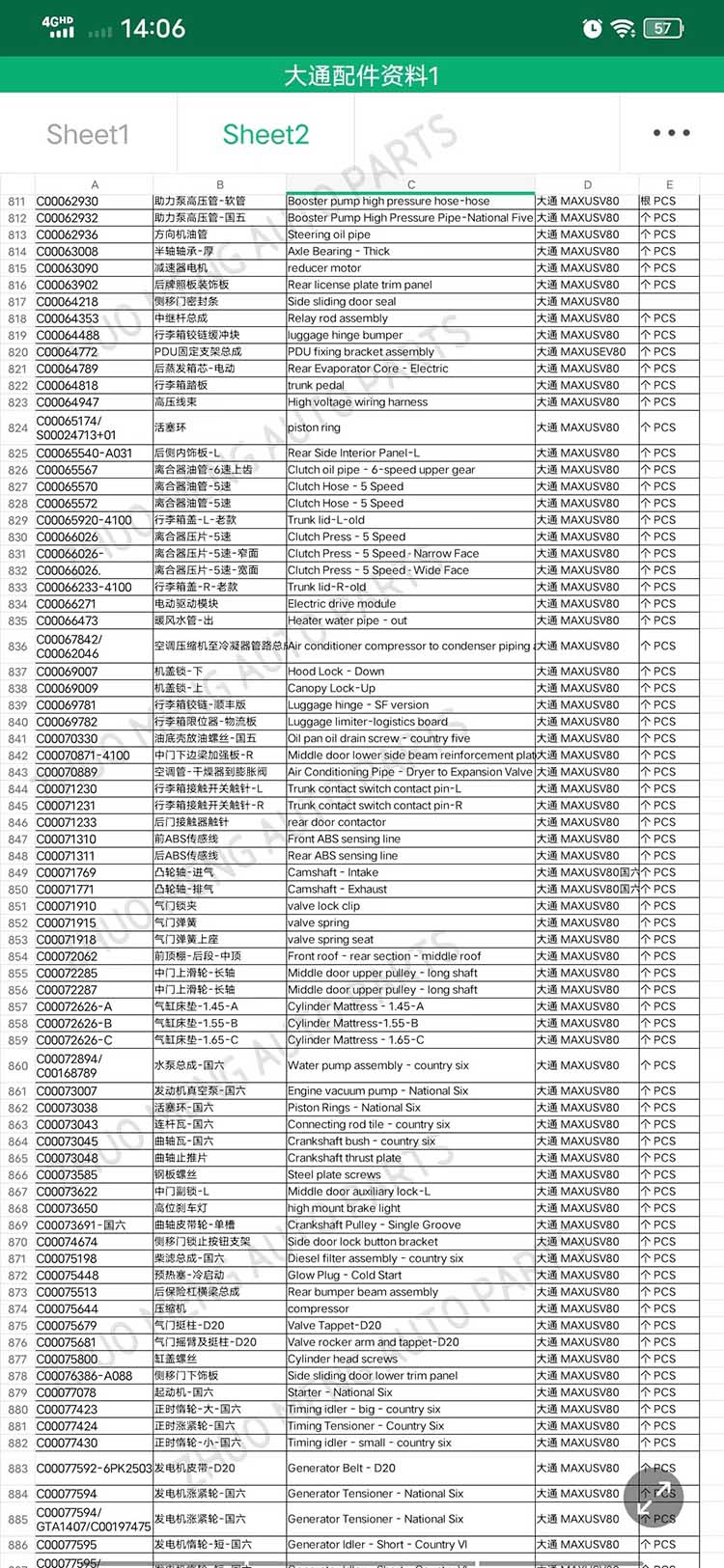
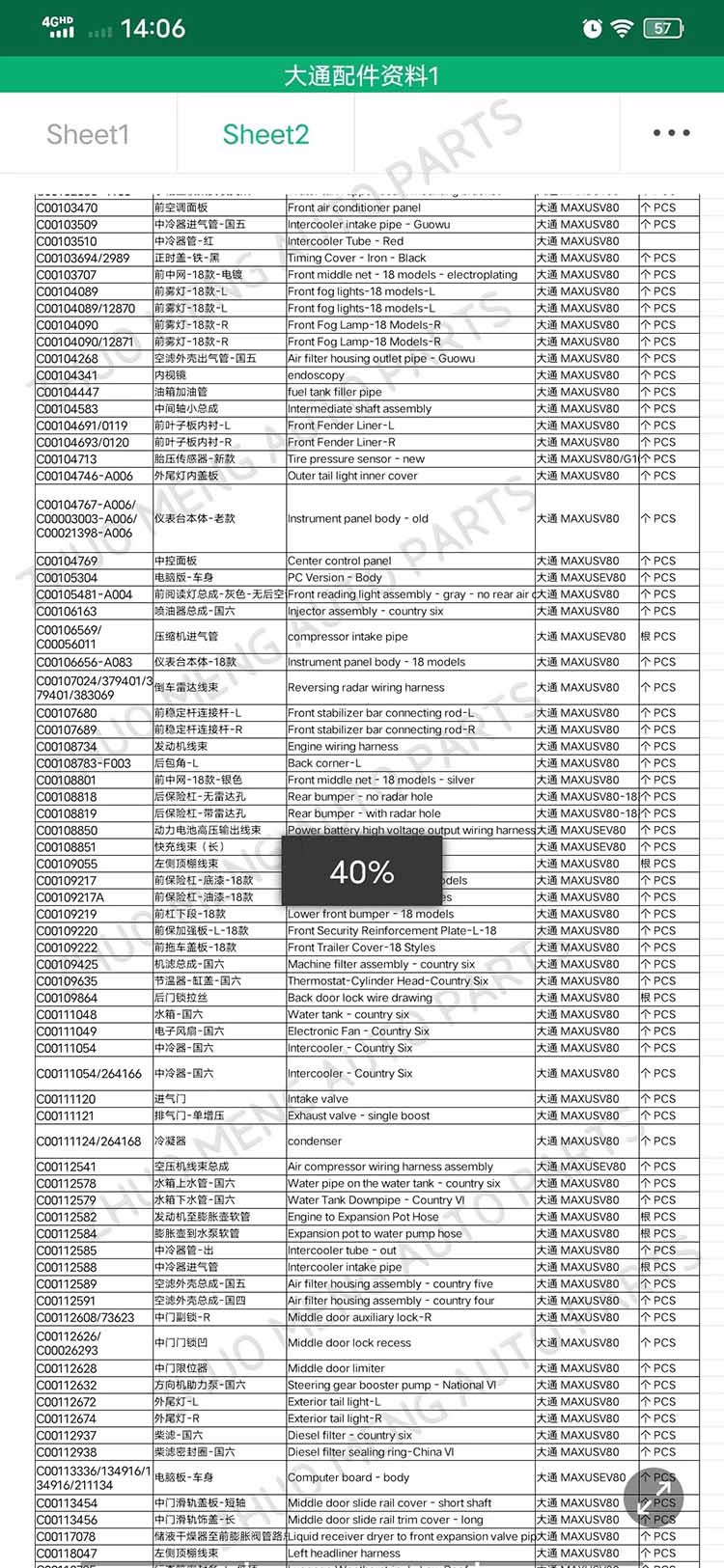
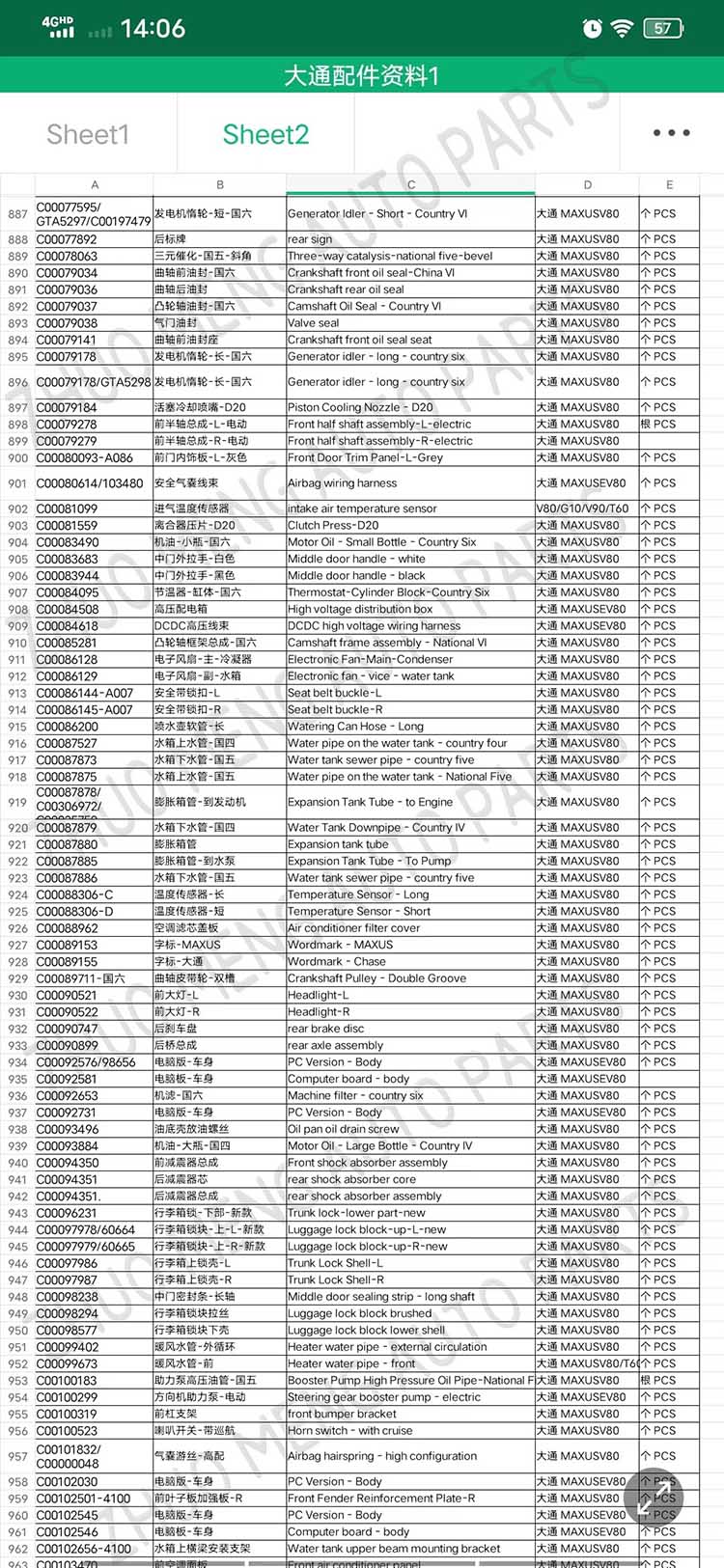
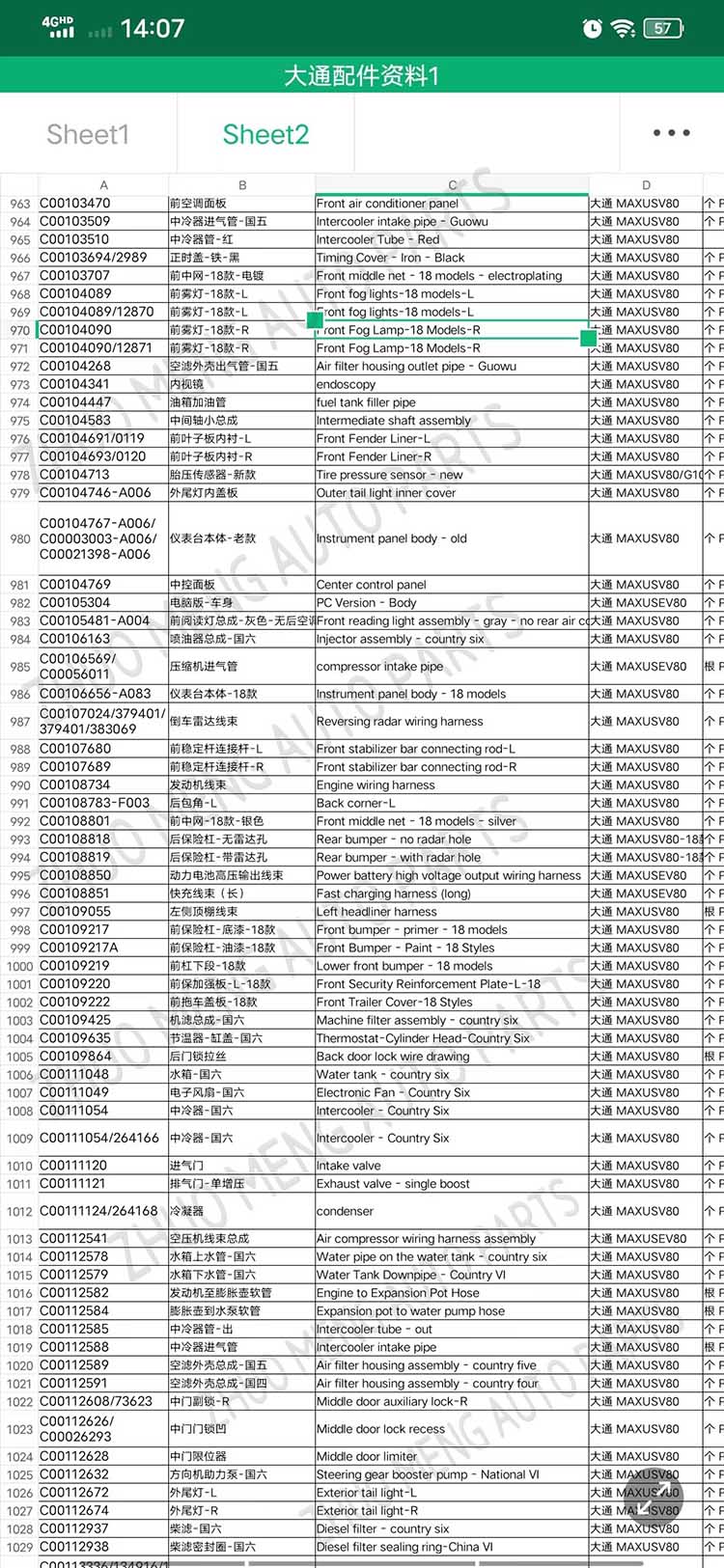
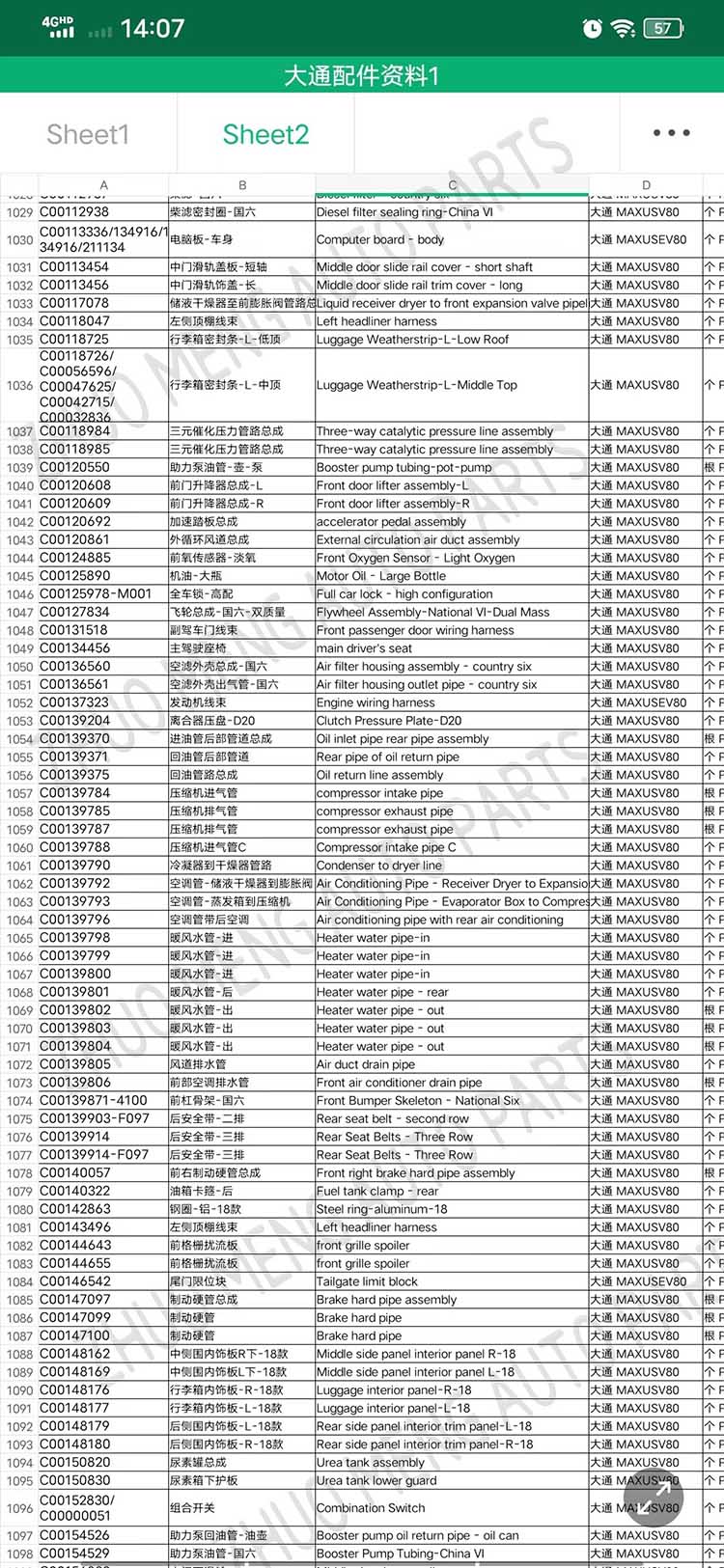
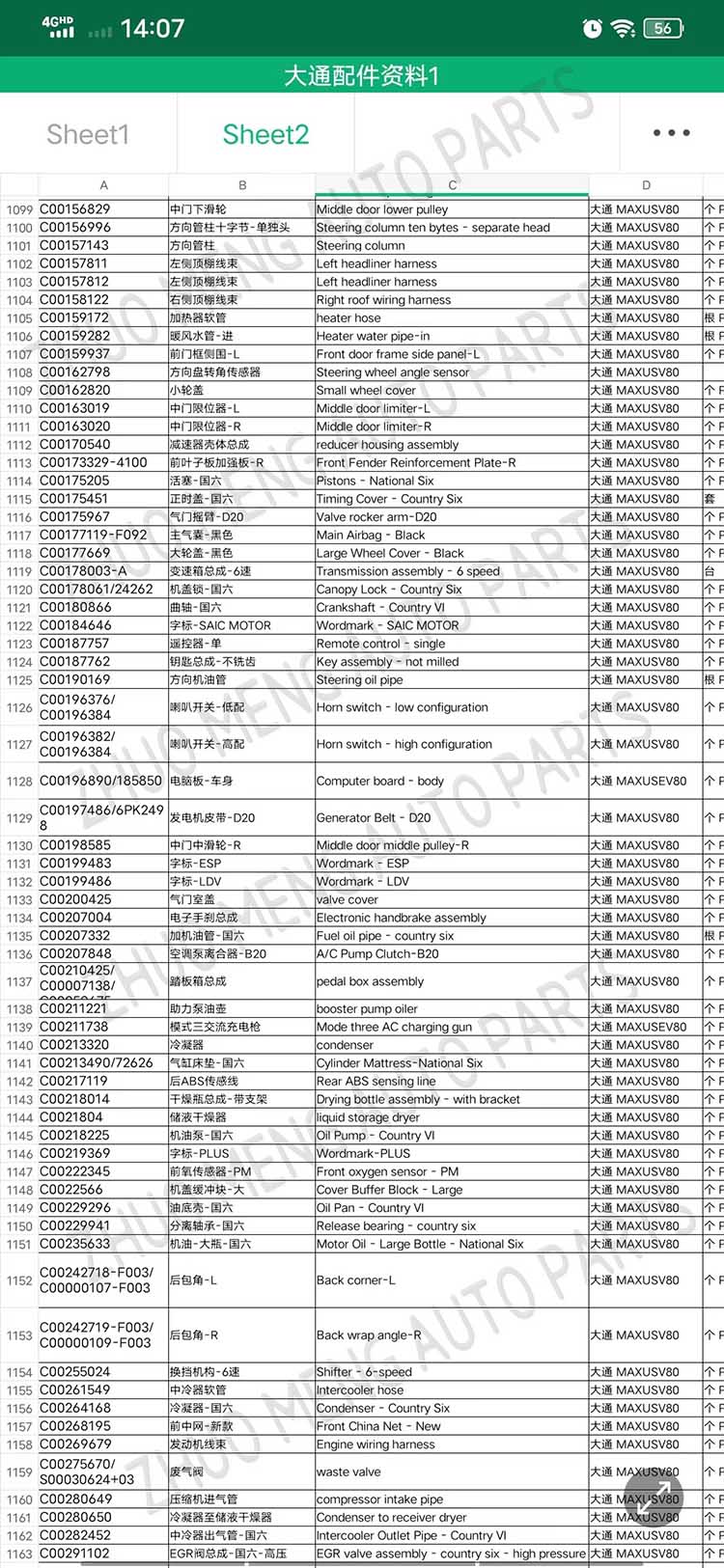
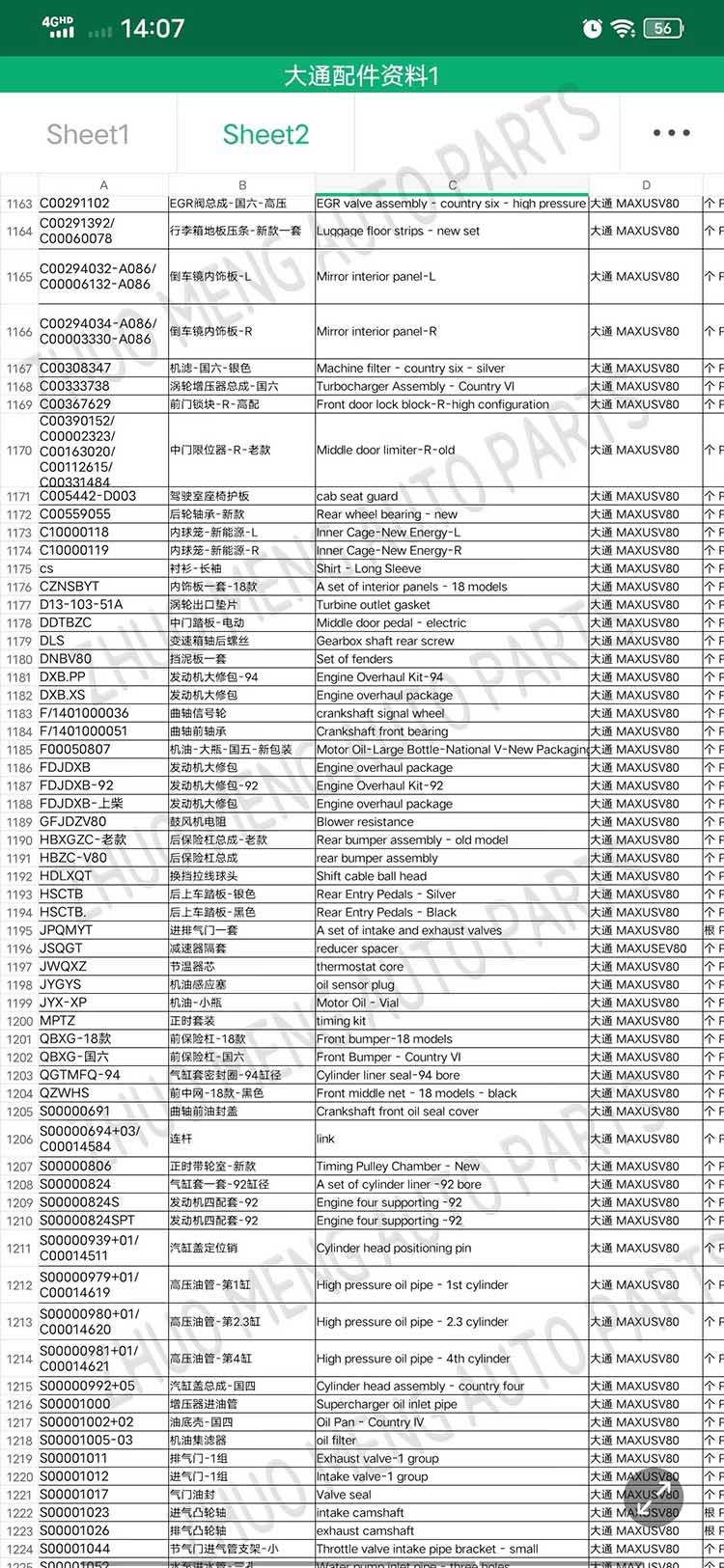
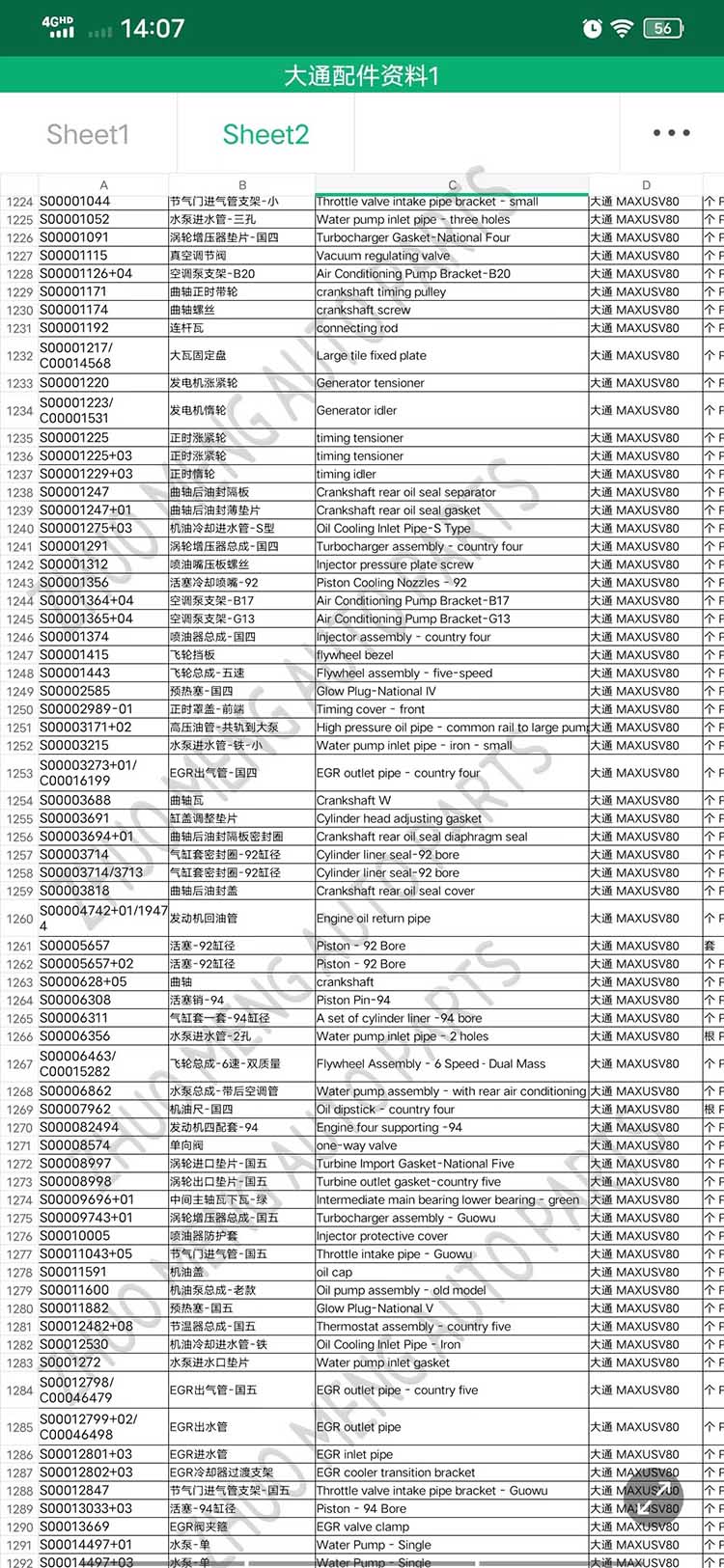
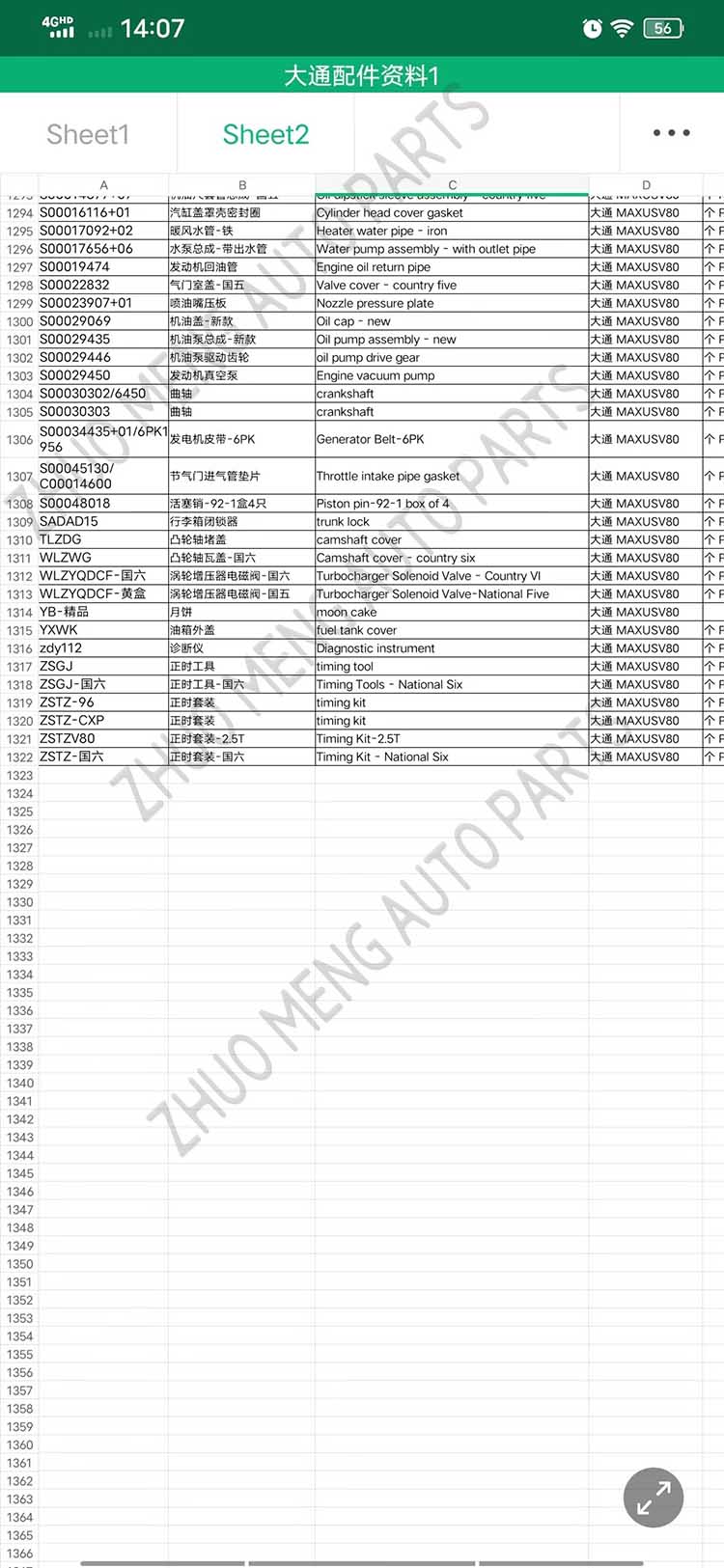
| Products OEM NO | C00014651 |
| Org of place | MADE IN CHINA |
| Brand | CSSOT /RMOEM/ORG/COPY |
| Lead time | Stock,if less 20 PCS,normal one month |
| Payment | TT Deposit |
| Company Brand | CSSOT |
| Application system | Cool system |
Products knowledge
Oil radiator is also called oil cooler. It is an oil cooling device used in diesel engines. According to the cooling method, oil coolers can be divided into water cooling and air cooling.
Generally speaking, engine oil generally refers to the collective name of engine oil, vehicle gear oil (MT) and hydraulic transmission oil (AT). Only hydraulic transmission oil needs an external oil cooler (that is, the oil radiator you said). ) for forced cooling, because the hydraulic transmission oil working in the automatic transmission needs to play the roles of hydraulic torque conversion, hydraulic transmission and lubrication and cleaning at the same time. The working temperature of the hydraulic transmission oil is relatively high. If it is cooled, the phenomenon of ablation of the transmission may occur, so the function of the oil cooler is to cool the hydraulic transmission oil to ensure that the automatic transmission can work normally.
Type
According to the cooling method, oil coolers can be divided into water cooling and air cooling. Water cooling is to introduce the coolant on the engine cooling system circuit into the oil cooler installed on the automatic transmission for cooling, or to introduce the hydraulic transmission oil into the lower water chamber of the radiator of the engine cooling system for cooling; The oil is introduced into the oil cooler installed on the windward side of the front grille for cooling [1].
Function The function of the oil radiator is to force the oil to cool, prevent the oil temperature from being too high and increase the oil consumption, and also prevent the oil from oxidizing and deteriorating.
Common faults and causes
The common failures of water-cooled oil radiators in use include copper pipe rupture, cracks in the front/rear cover, gasket damage, and internal blockage of the copper pipe. The failure of copper tube rupture and front and rear cover cracks is mostly caused by the operator’s failure to release the cooling water inside the diesel engine body in winter. When the above components are damaged, there will be oil in the water cooler and cooling water in the oil inside the oil pan during the operation of the diesel engine. When the diesel engine is running, if the pressure of the oil is greater than the pressure of the cooling water, the oil will enter the cooling water through the hole in the core, and with the circulation of the cooling water, the oil will enter the water cooler. When the diesel engine stops rotating, the cooling water level is high, and its pressure is greater than the pressure of the oil. The fatal cooling water escapes into the oil through the hole in the core, and finally enters the oil pan. If the operator can’t find this kind of fault in time, as the diesel engine continues to run, the lubricating effect of the oil will be lost, and finally the diesel engine will have an accident such as tile burning.
After the individual copper tubes inside the radiator are blocked by scale and impurities, it will affect the heat dissipation effect of the oil and the circulation of the oil, so it should be cleaned regularly.
Overhaul
During the operation of the diesel engine, if it is found that the cooling water enters the oil pan and there is oil in the water radiator, this failure is generally caused by the damage to the core of the water-cooled oil cooler.
The specific maintenance methods are as follows:
1. After draining the waste oil inside the radiator, remove the oil cooler. After the removed cooler is leveled, fill the cooler with water through the water outlet of the oil cooler. During the test, the water inlet was blocked, and the other side used a high-pressure air cylinder to inflate the inside of the cooler. If it is found that there is water coming out from the oil inlet and outlet of the oil radiator, it means that the inner core of the cooler or the sealing ring of the side cover is damaged.
2. Remove the front and rear covers of the oil radiator, and take out the core. If the outer layer of the core is found to be damaged, it can be repaired by brazing. If the inner layer of the core is found to be damaged, a new core should generally be replaced or both ends of the same core should be blocked. When the side cover is cracked or broken, it can be used after welding with a cast iron electrode. If the gasket is damaged or aged, it should be replaced. When the copper tube of the air-cooled oil radiator is de-soldered, it is generally repaired by brazing.
OUR EXHIBITION




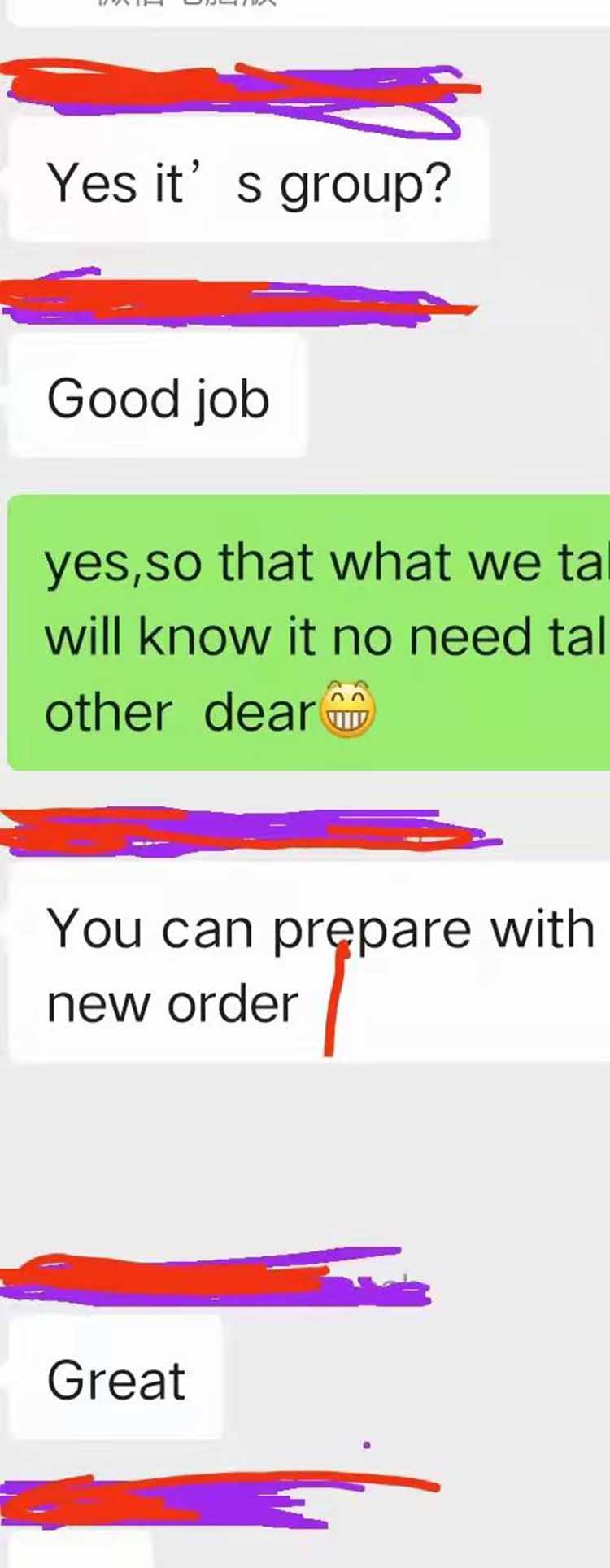
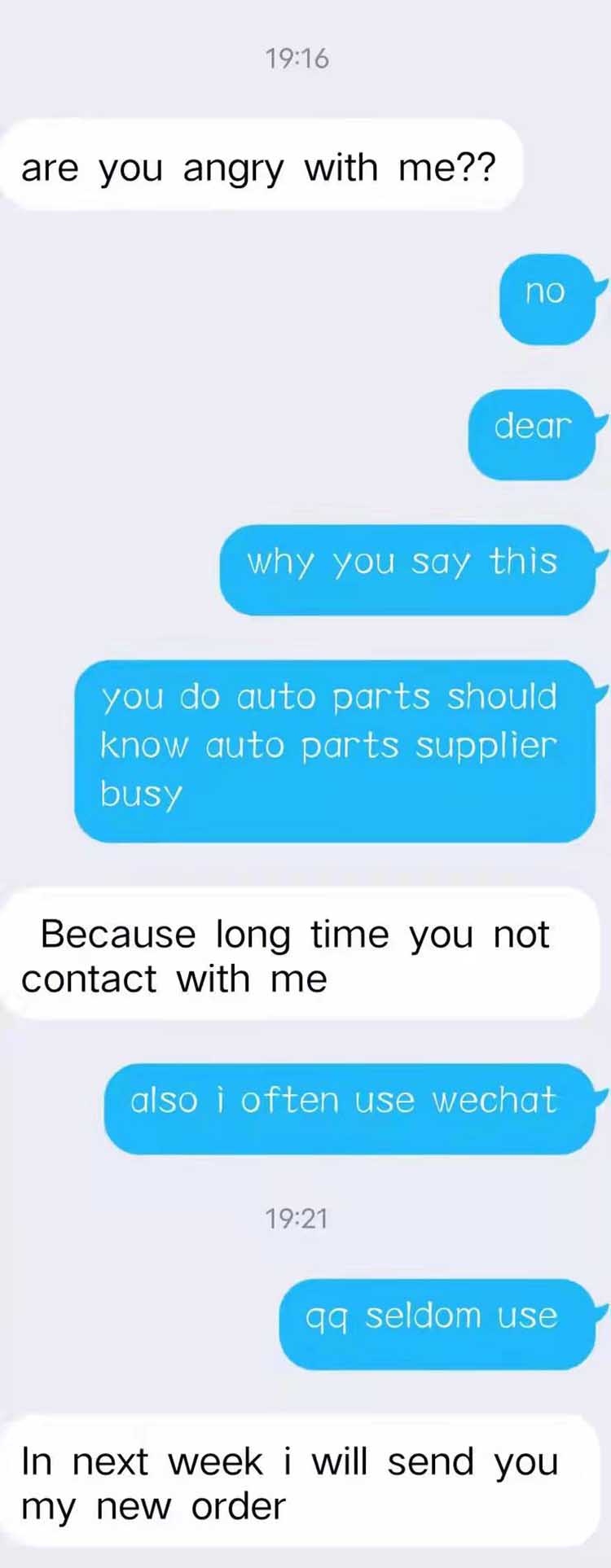
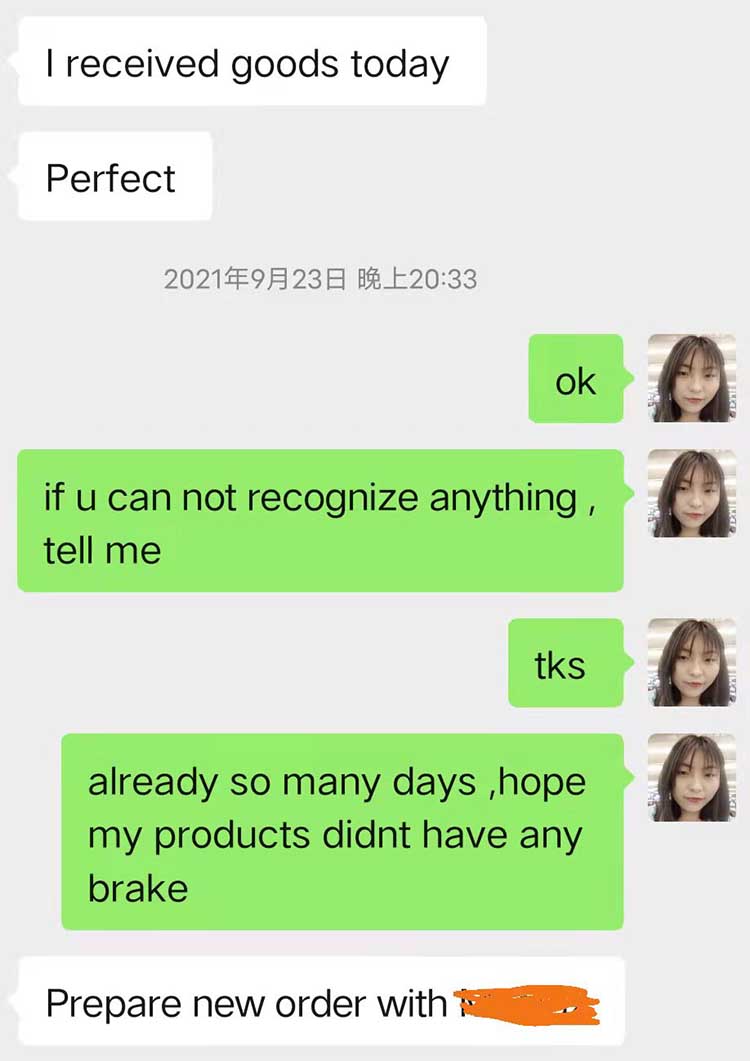
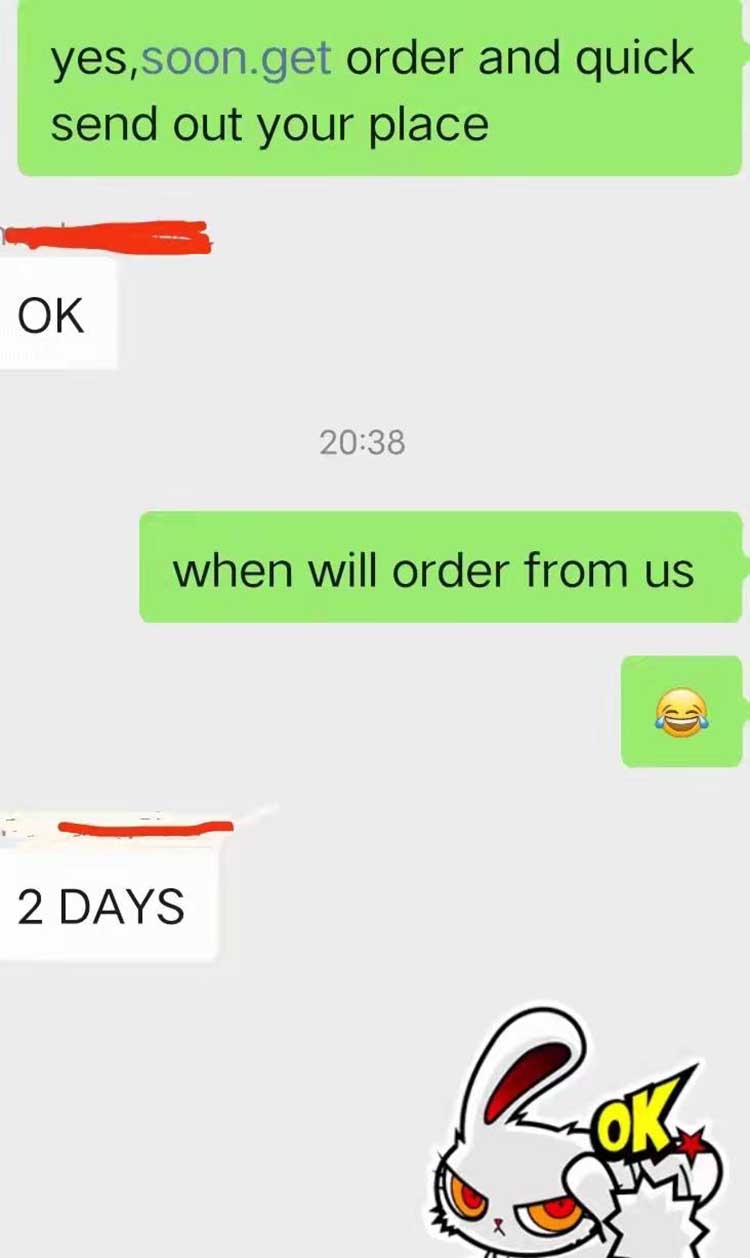
Good Feetback
Products catalog
Related products


Product detail pictures:
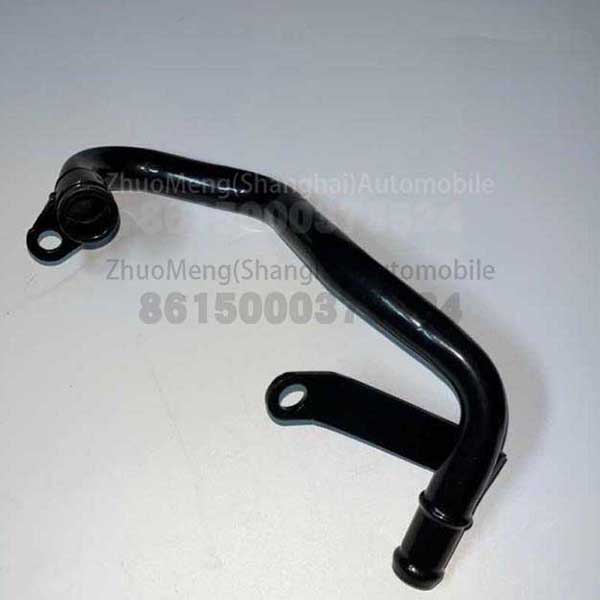
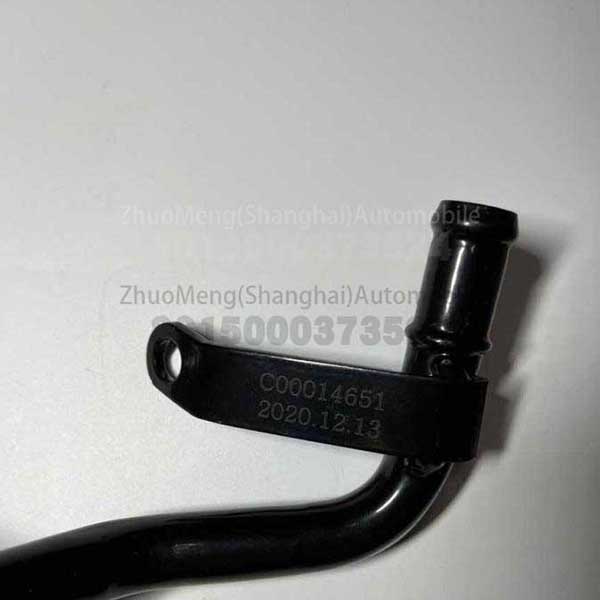




Related Product Guide:
Our company promises all users of the first-class products and the most satisfying post-sale service. We warmly welcome our regular and new customers to join us for Newly Arrival Mg Zx Accessories Wholesale - SAIC MAXUS V80 Oil radiator – iron water pipe – VI Maxus wholesale supplier – Zhuomeng , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Chile, America, Venezuela, Our stock have valued 8 million dollar , you can find the competitive parts within short delivery time. Our company is not only your partner in business, but also our company is your assistant in the coming corporation.
With a positive attitude of "regard the market, regard the custom, regard the science", the company works actively to do research and development. Hope we have a future business relationships and achieving mutual success.