New Fashion Design for Mg3 Spare Parts Wholesale - factory price SAIC MAXUS V80 front evaporator core C00013620 – Zhuomeng
New Fashion Design for Mg3 Spare Parts Wholesale - factory price SAIC MAXUS V80 front evaporator core C00013620 – Zhuomeng Detail:
Products information
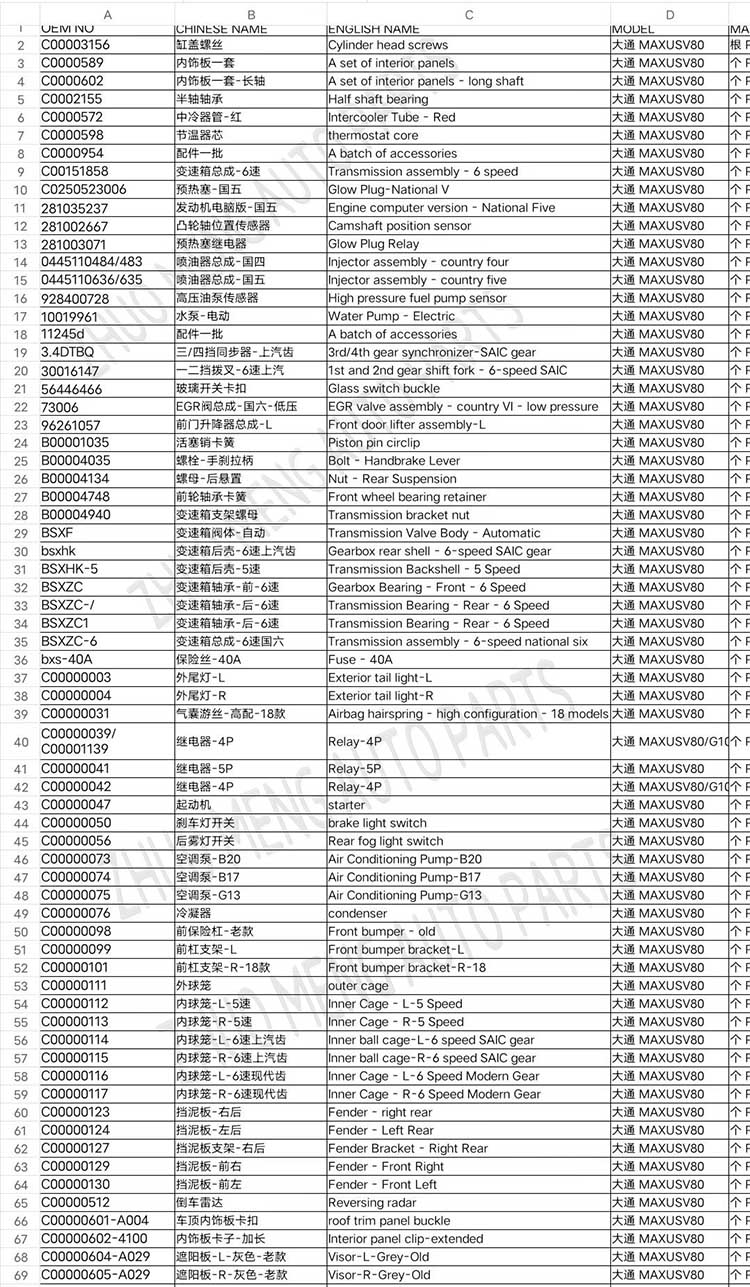
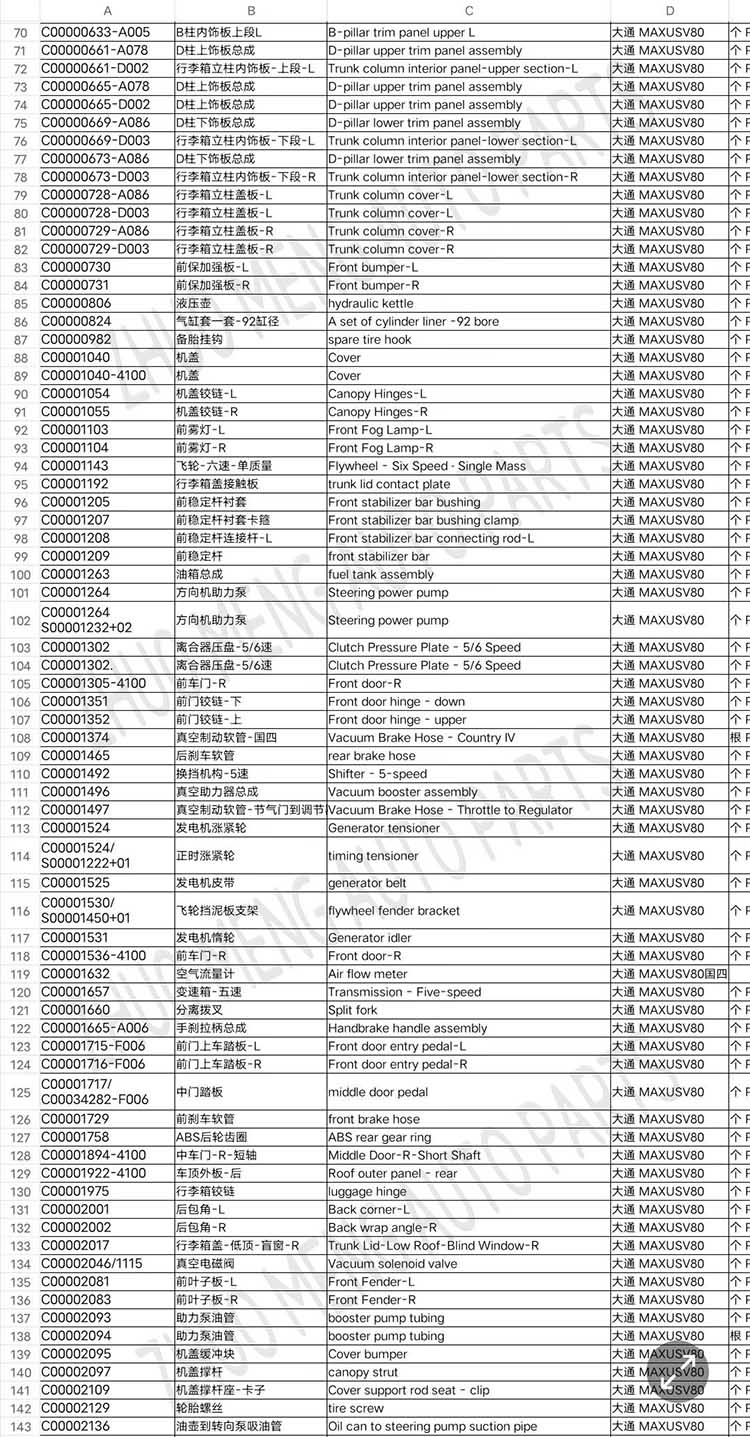
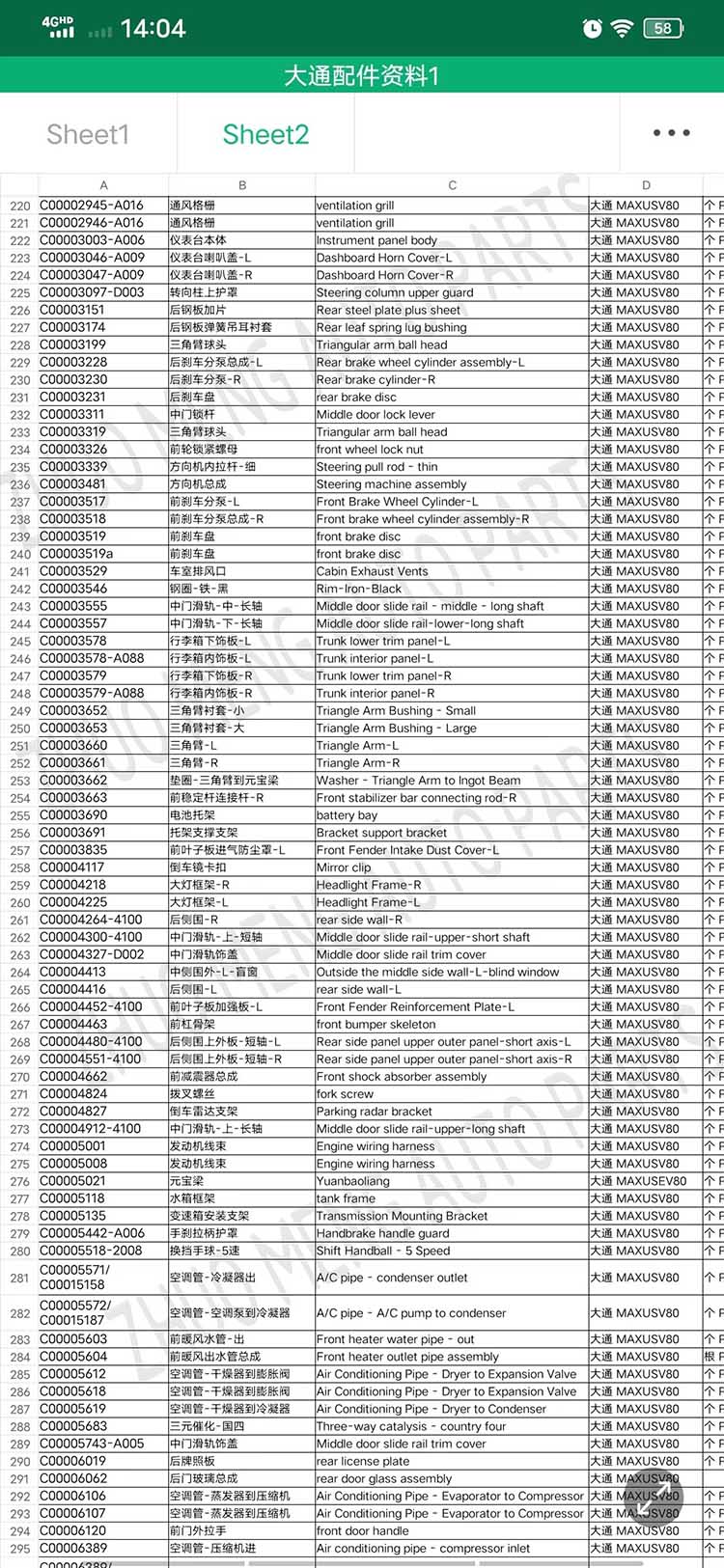
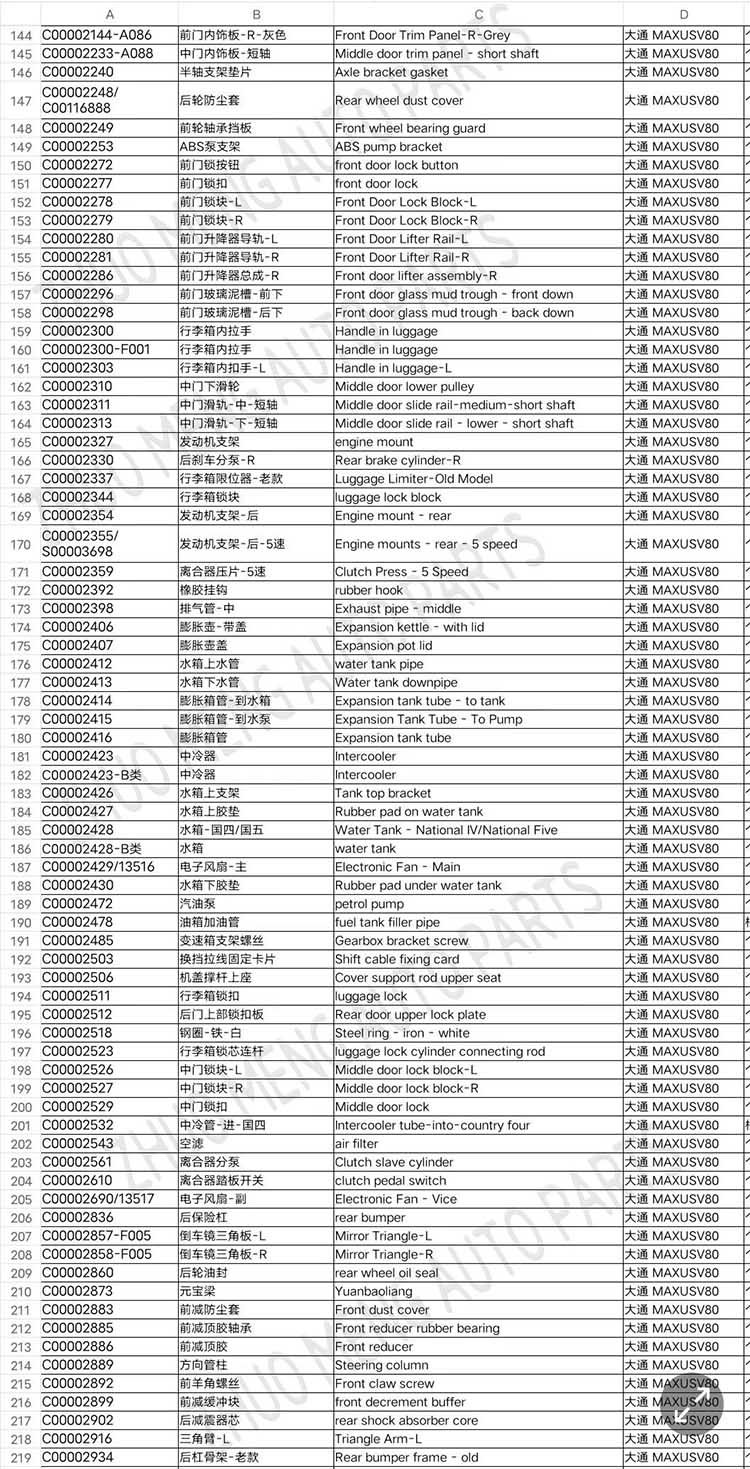
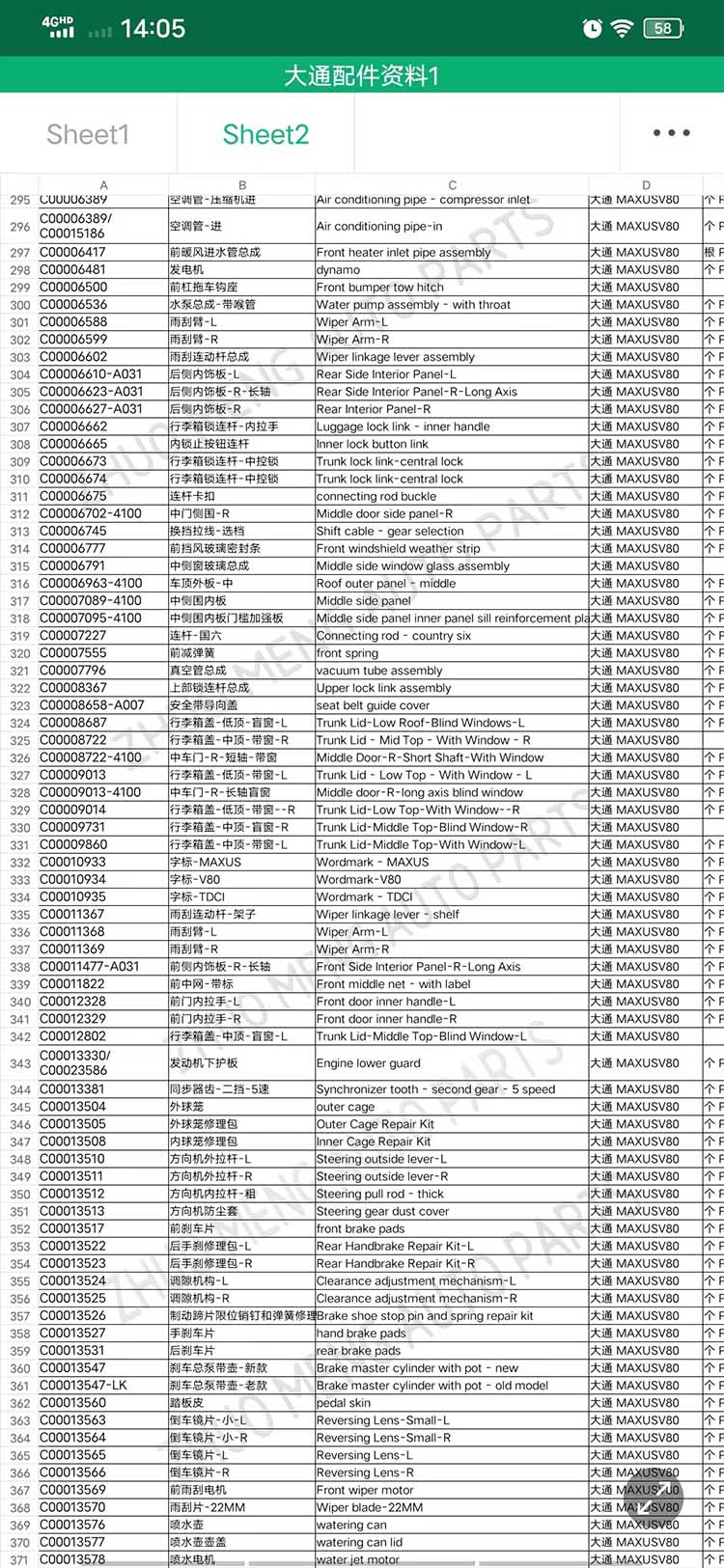
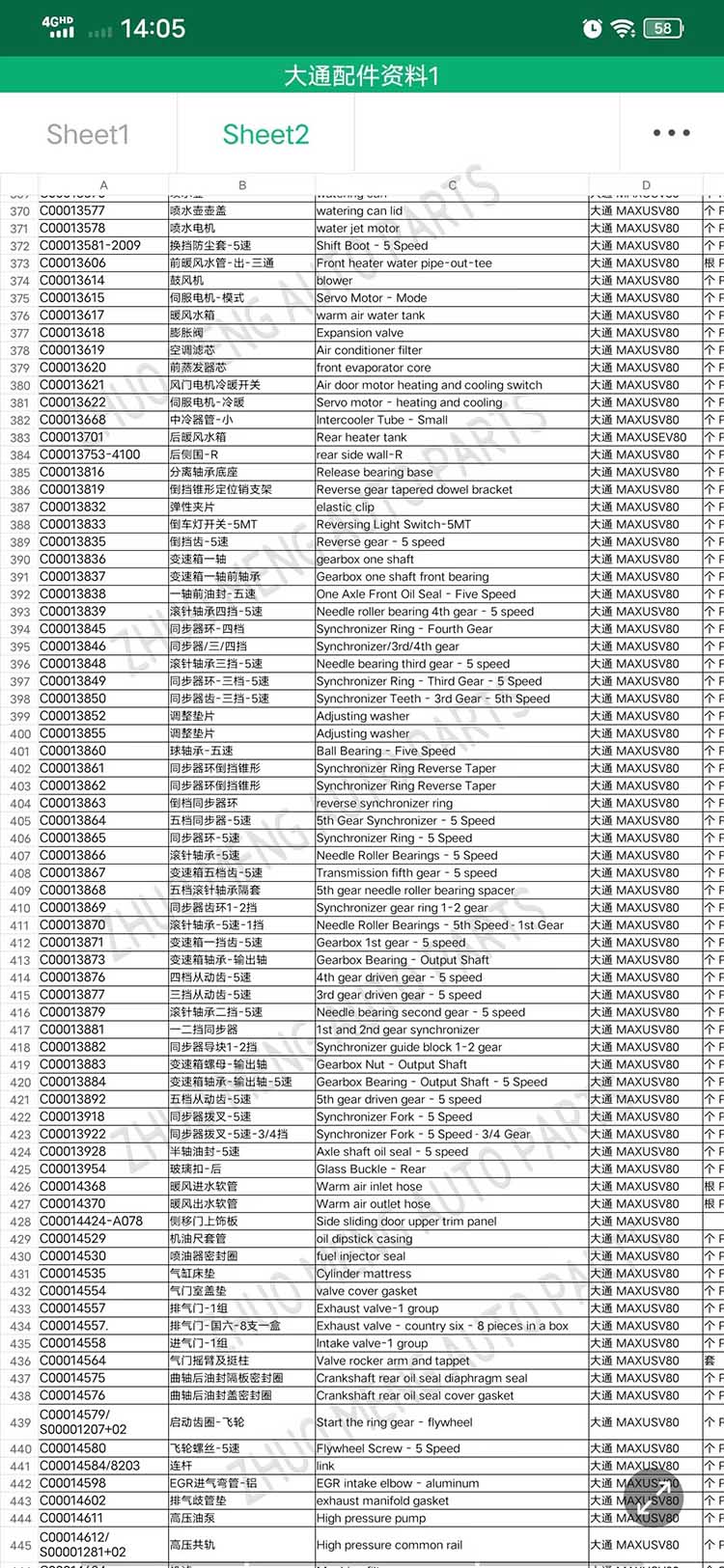
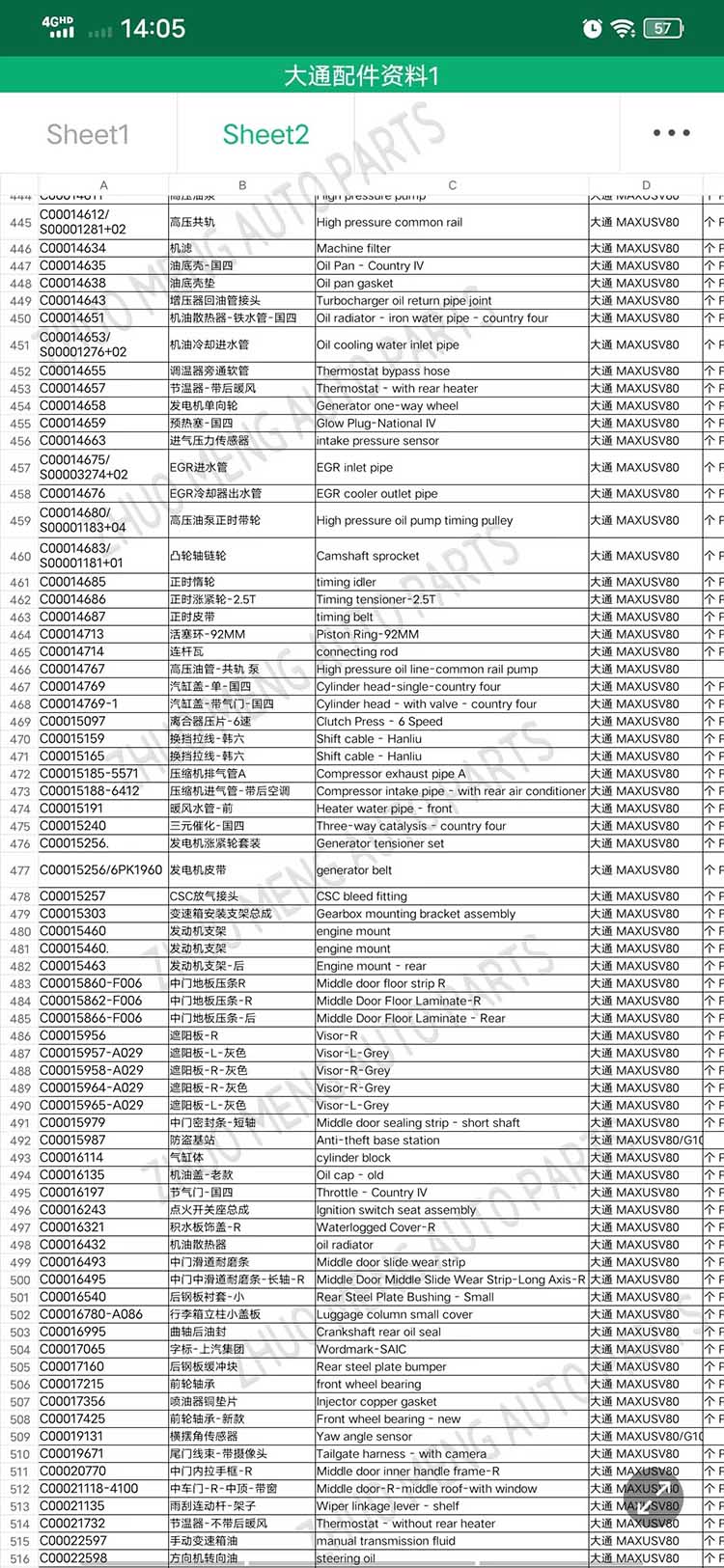
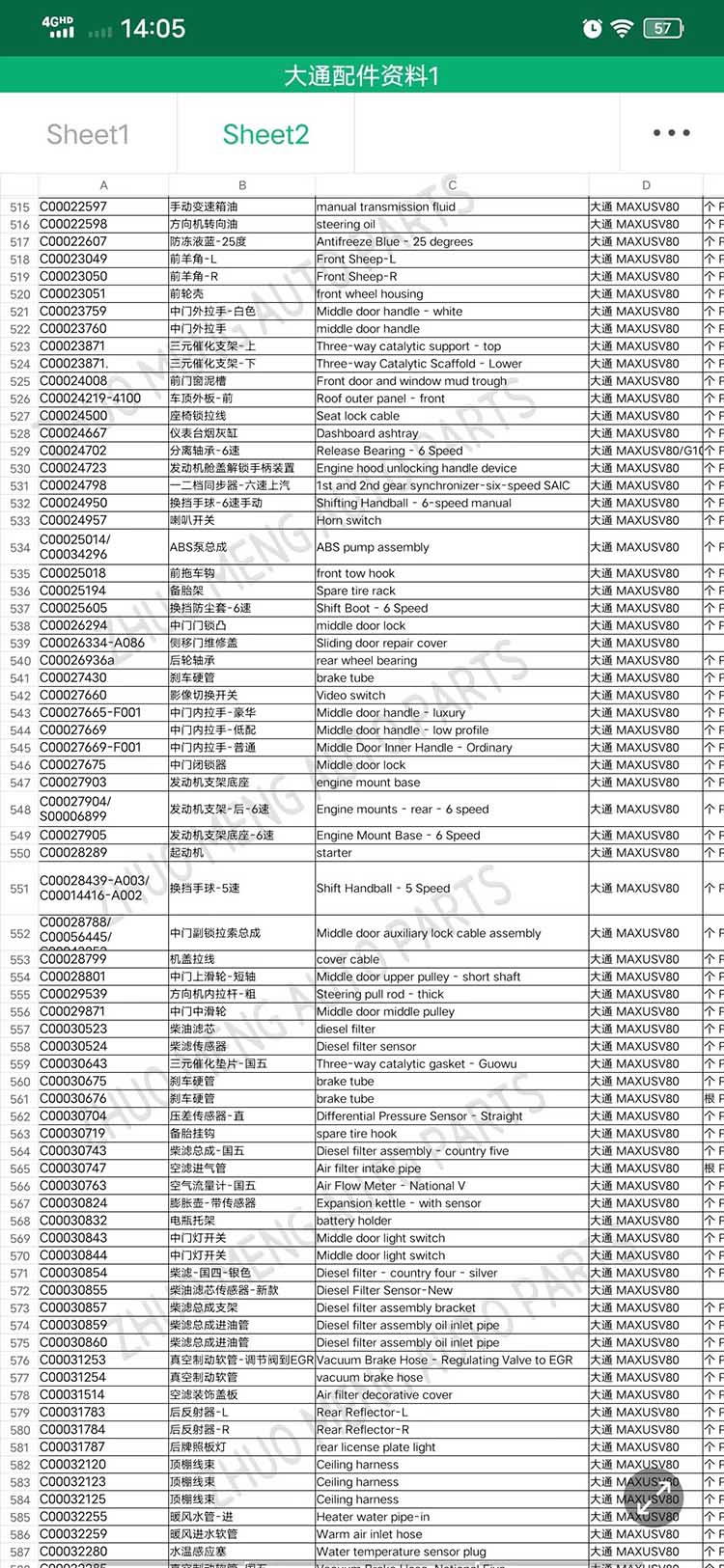
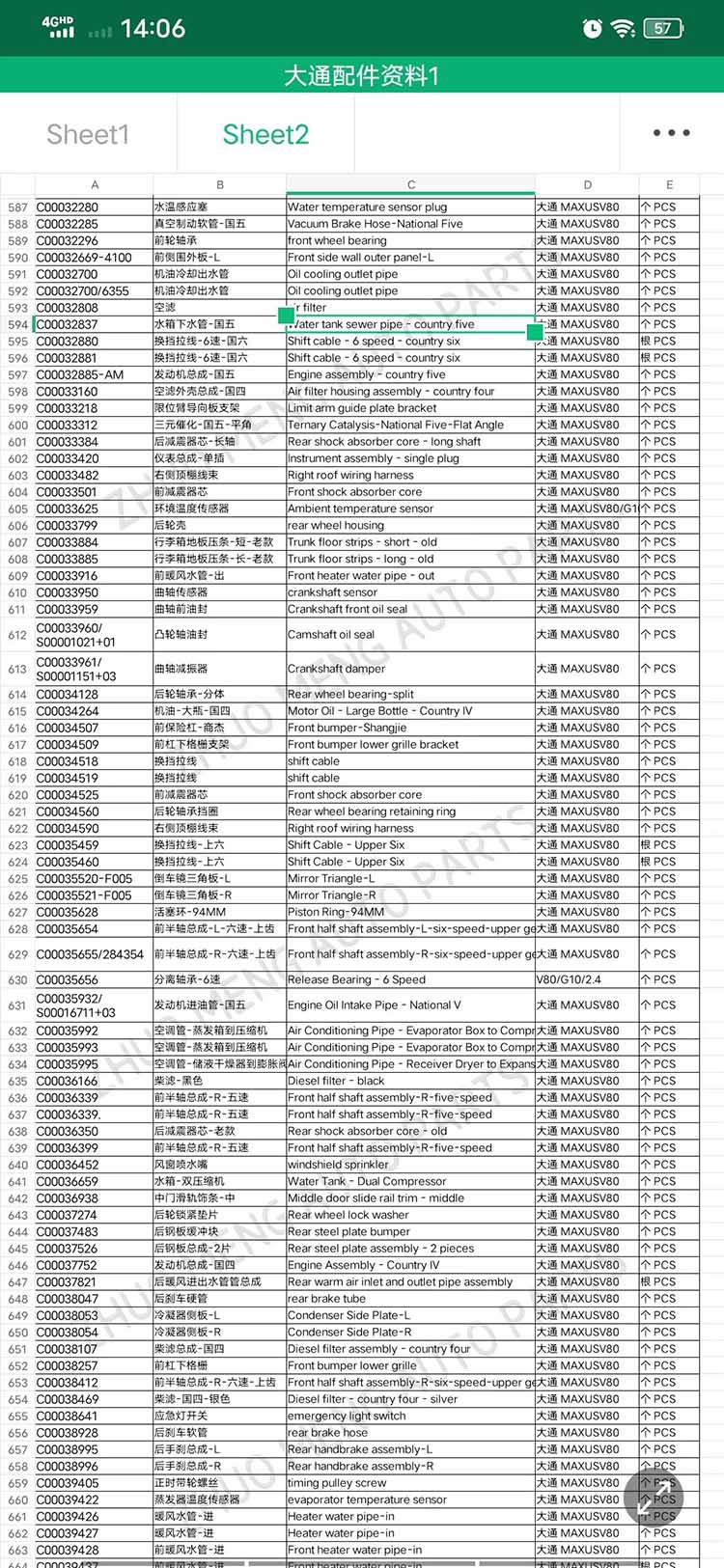
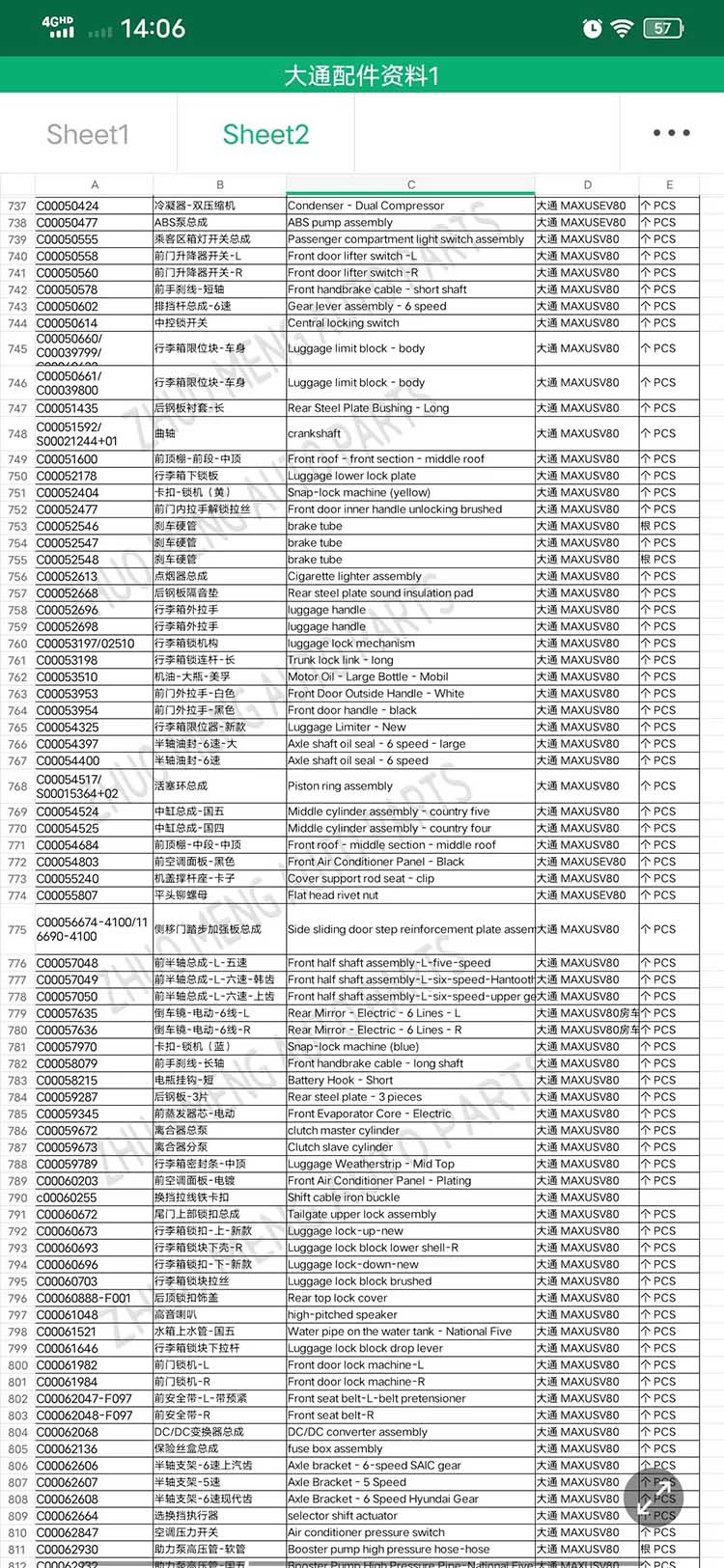
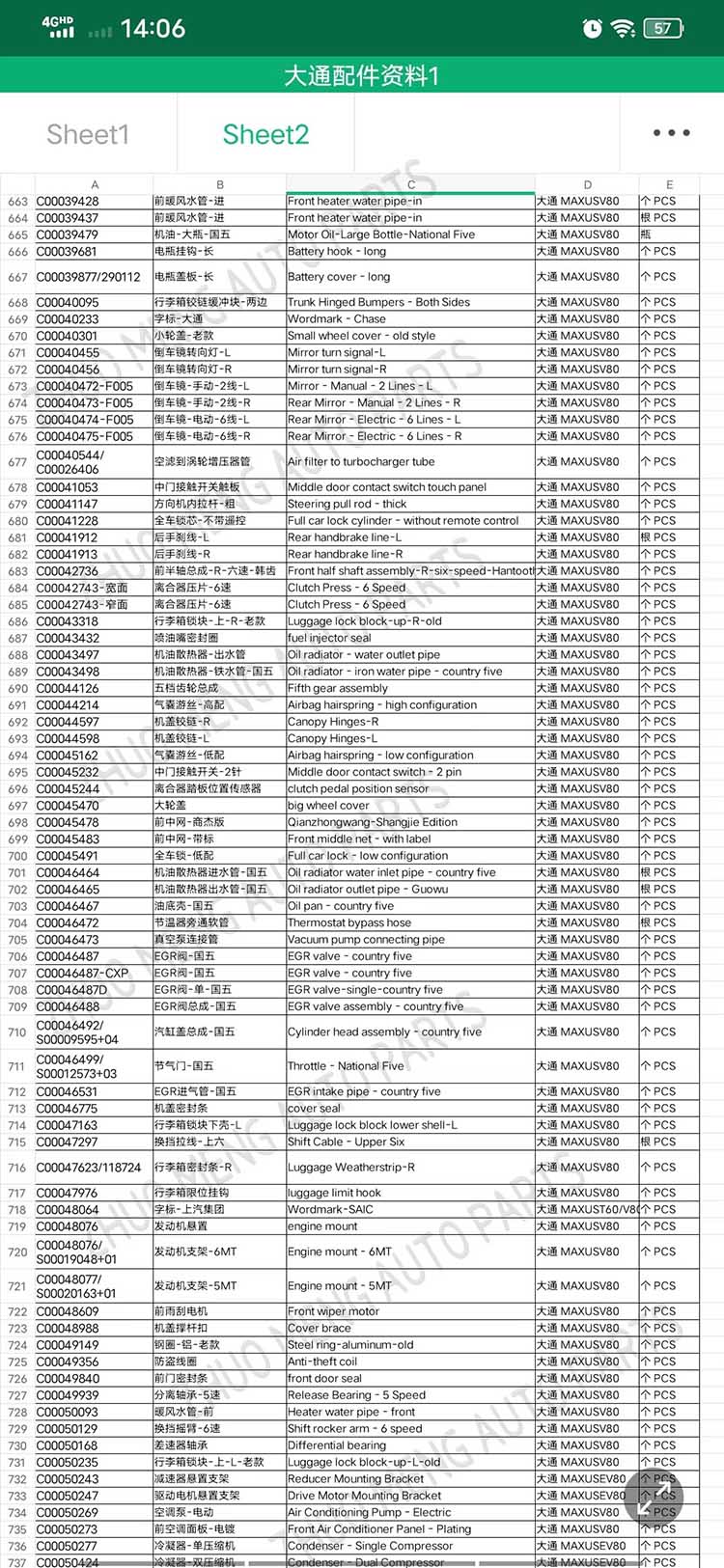
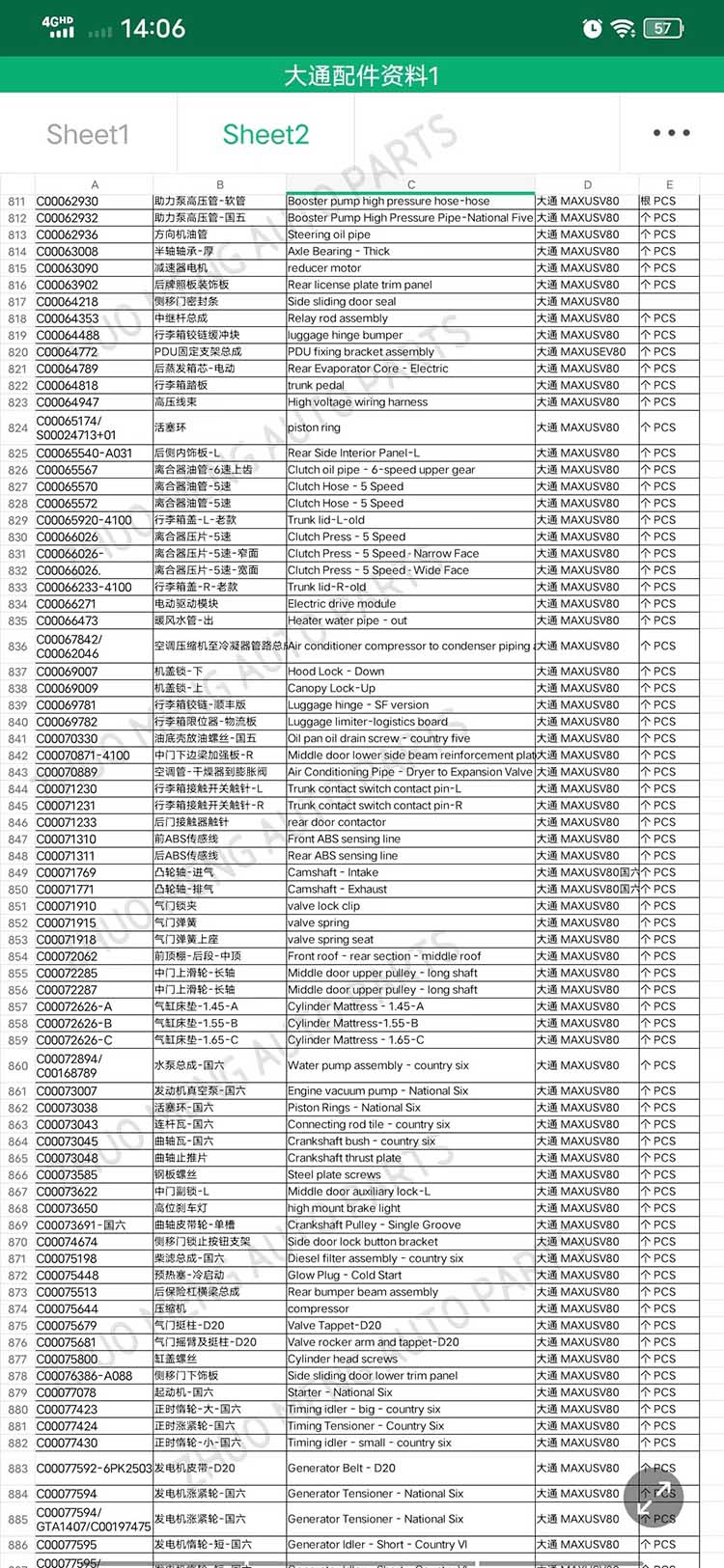
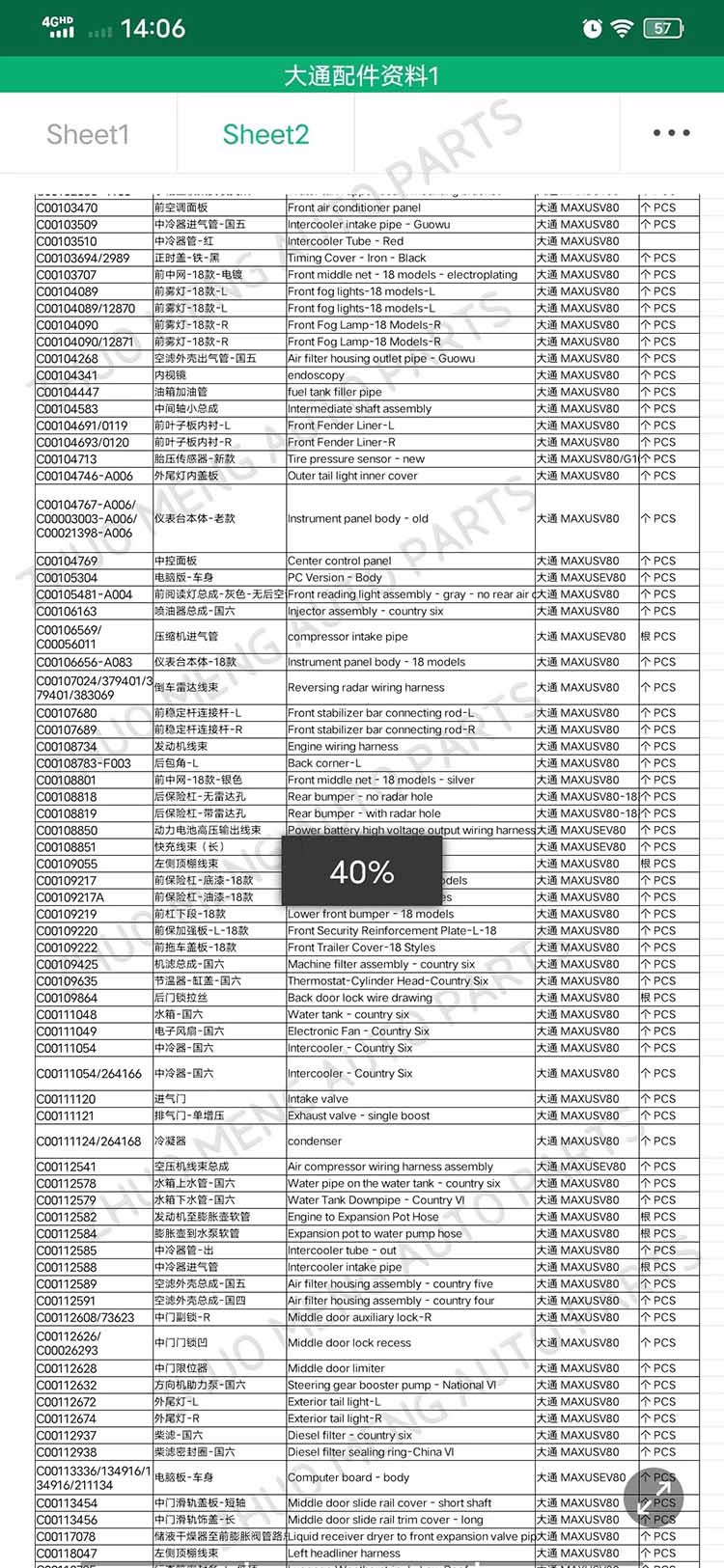
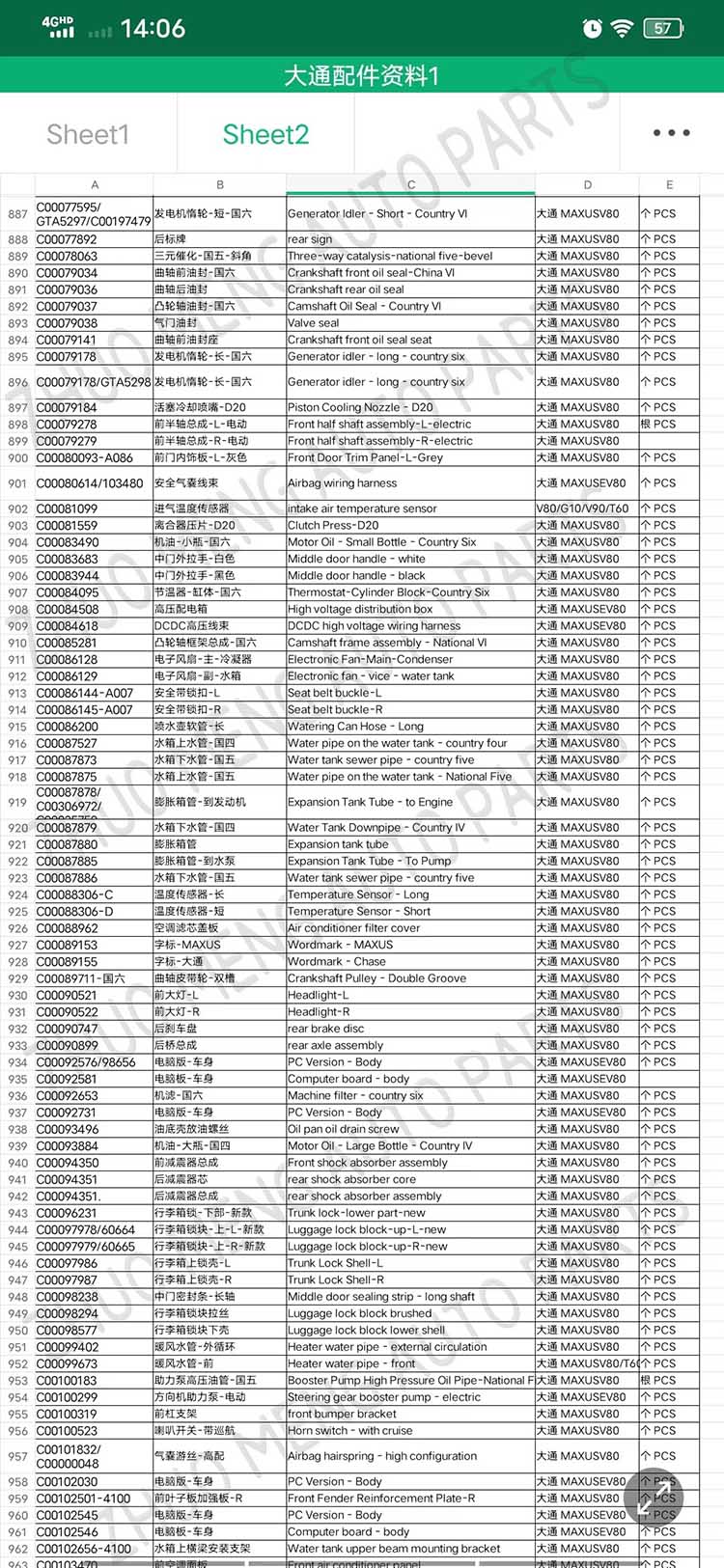
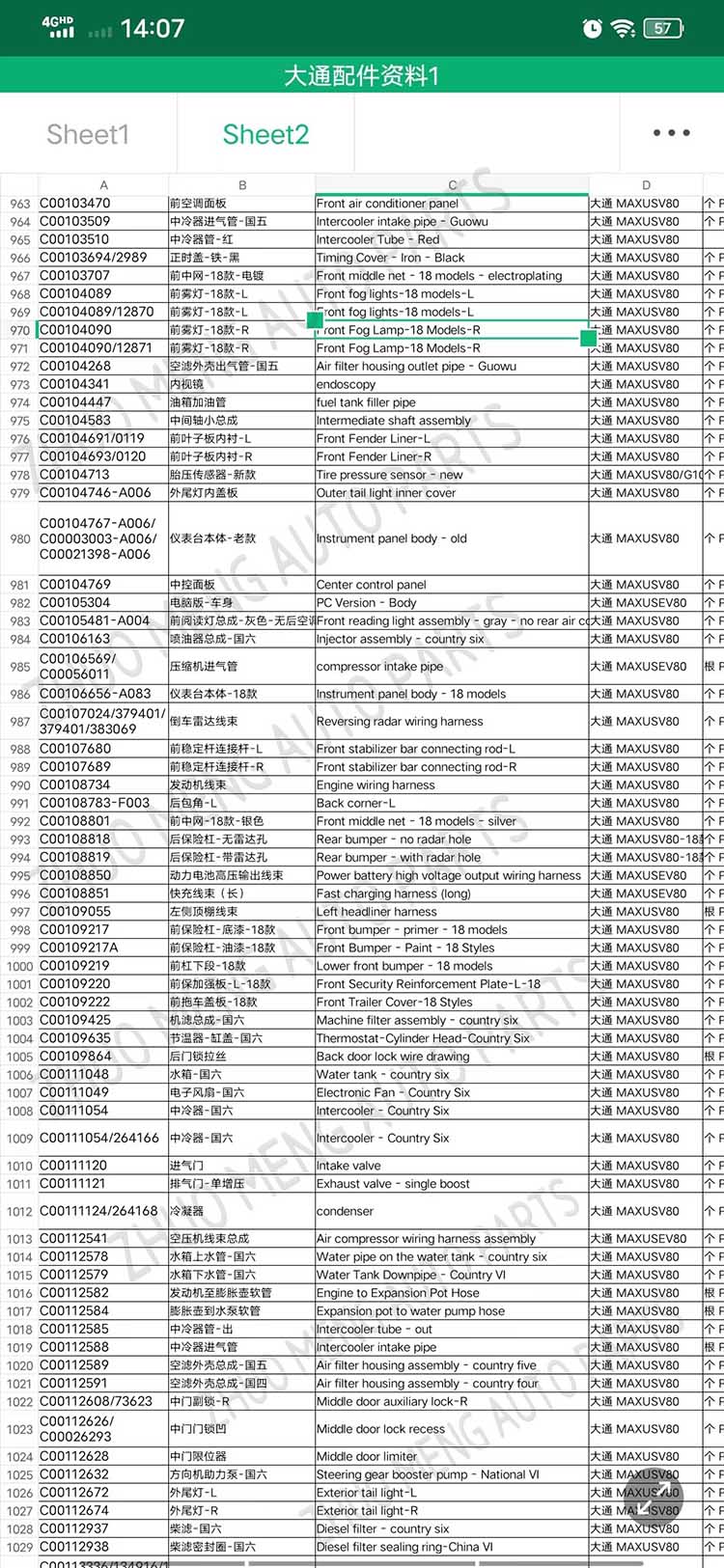
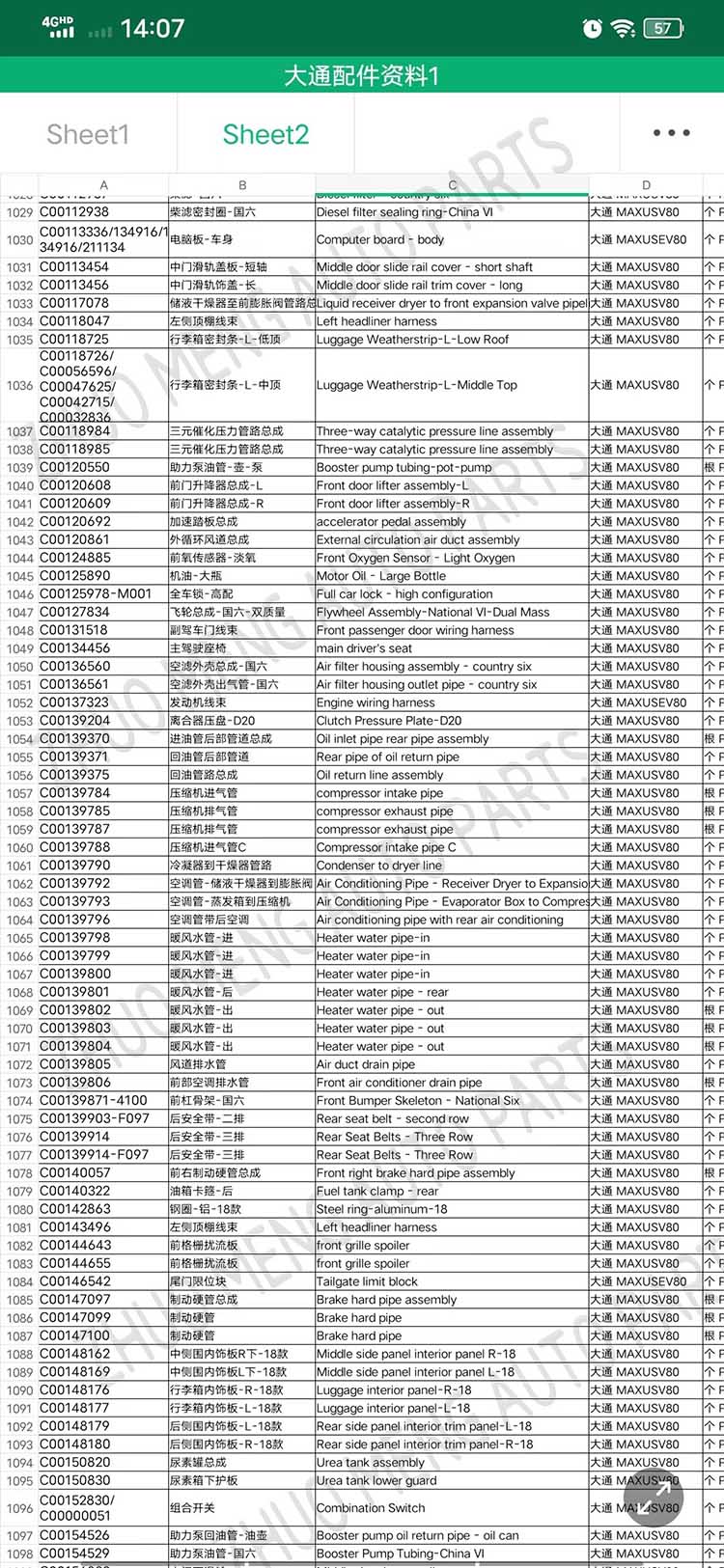
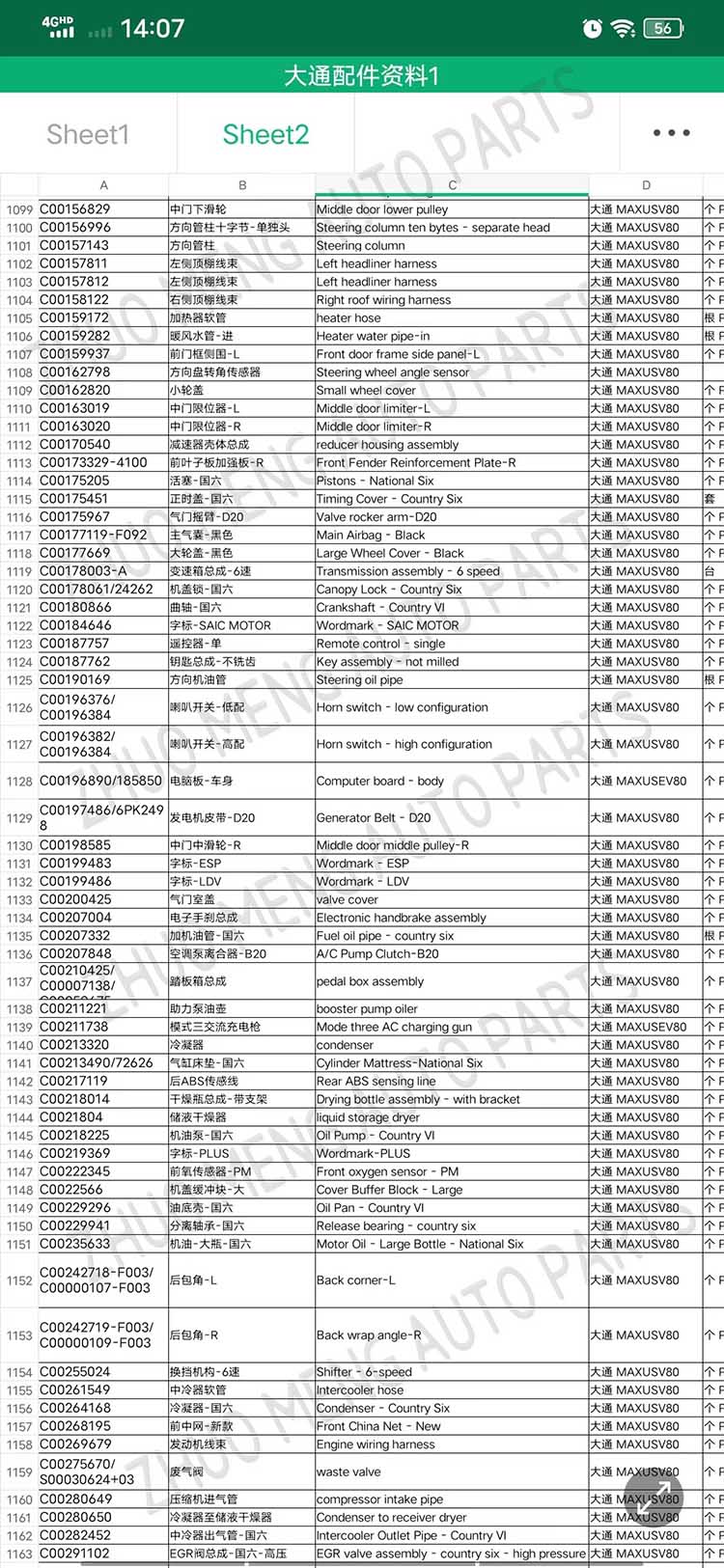
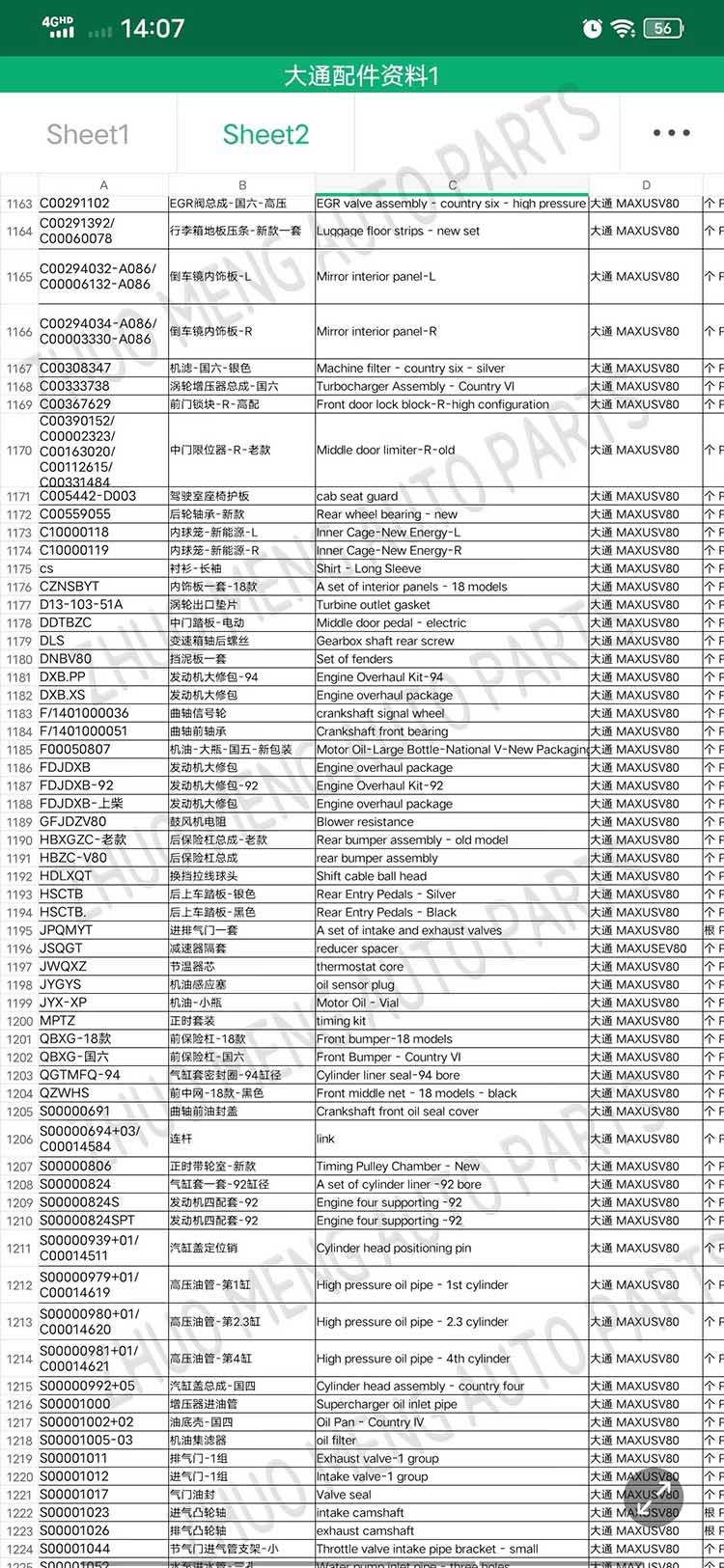
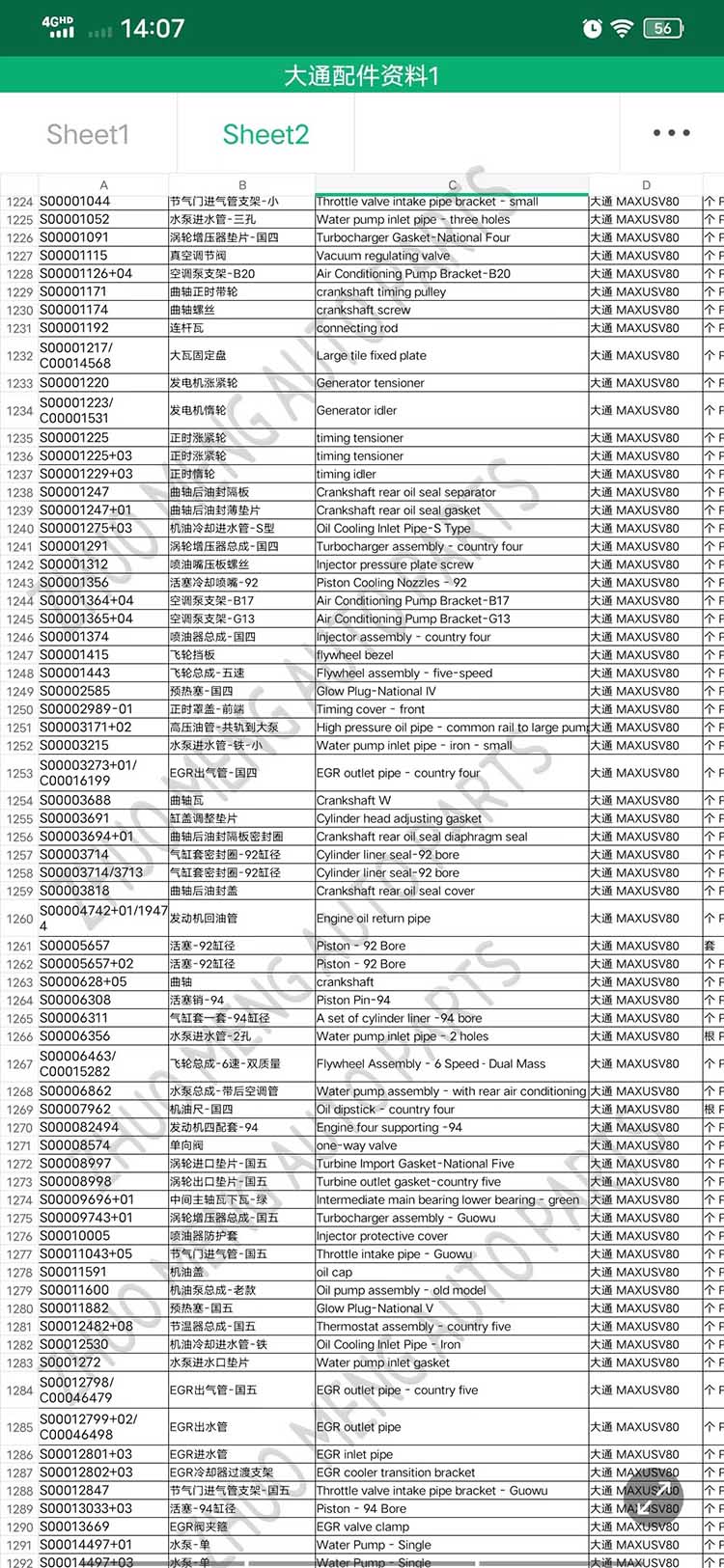
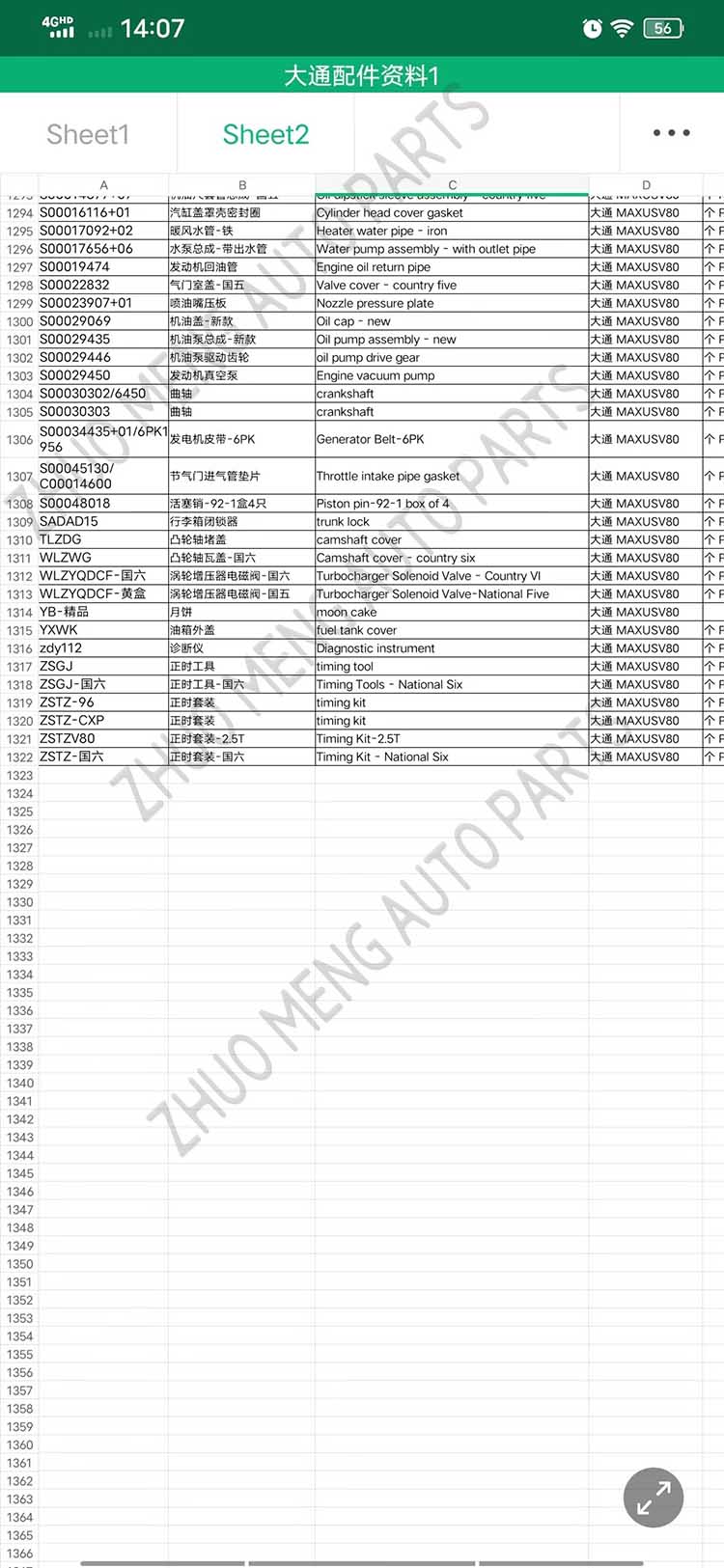
| Products name | front evaporator core |
| Products application | SAIC MAXUS V80 |
| Products OEM NO | C00013620 |
| Org of place | MADE IN CHINA |
| Brand | CSSOT /RMOEM/ORG/COPY |
| Lead time | Stock,if less 20 PCS,normal one month |
| Payment | TT Deposit |
| Company Brand | CSSOT |
| Application system | Cool system |
Products knowledge
Evaporation is the physical process of converting a liquid into a gas. Generally speaking, an evaporator is an object that converts a liquid substance into a gaseous state. There are a large number of evaporators in the industry, and the evaporator used in the refrigeration system is one of them. The evaporator is a very important part of the four major components of refrigeration. The low-temperature condensed liquid passes through the evaporator to exchange heat with the outside air, vaporizes and absorbs heat, and achieves the effect of refrigeration. The evaporator is mainly composed of a heating chamber and an evaporation chamber. The heating chamber provides the liquid with the heat required for vaporization, and promotes the liquid to boil and vaporize; the vaporization chamber completely separates the gas-liquid two phases.
The vapor generated in the heating chamber has a large amount of liquid foam. After reaching the evaporation chamber with a larger space, these liquids are separated from the vapor by self-condensation or the action of a demister. Usually the demister is located at the top of the evaporation chamber.
The evaporator is divided into three types according to the operating pressure: normal pressure, pressurized and decompressed. According to the movement of the solution in the evaporator, it can be divided into: ① circulation type. The boiling solution passes through the heating surface for many times in the heating chamber, such as central circulation tube type, hanging basket type, external heating type, Levin type and forced circulation type. ②One-way type. The boiling solution passes through the heating surface once in the heating chamber without circulating flow, that is, the concentrated liquid is discharged, such as rising film type, falling film type, stirring film type and centrifugal film type. ③ Direct contact type. The heating medium is in direct contact with the solution to transfer heat, such as a submerged combustion evaporator. During the operation of the evaporation device, a large amount of heating steam is consumed. In order to save the heating steam, a multi-effect evaporation device and a vapor recompression evaporator can be used. Evaporators are widely used in chemical, light industry and other sectors.
A vaporizer used in medicine, volatile inhalation anesthetics are liquid at room temperature. The vaporizer can effectively vaporize the volatile anesthetic liquid into gas, and can precisely adjust the concentration of the anesthetic vapor output. The vaporization of anesthetics requires heat, and the temperature around the vaporizer is a major factor in determining the rate of vaporization of volatile anesthetics. Contemporary anesthesia machines widely use temperature-flow compensation evaporators, that is, when the temperature or fresh air flow changes, the evaporation rate of volatile inhalation anesthetics can be kept constant through an automatic compensation mechanism, so as to ensure that the inhalation anesthetics leave the evaporator. The output concentration is stable. Due to the different physical properties such as the boiling point and saturated vapor pressure of different volatile inhalation anesthetics, vaporizers have drug specificity, such as enflurane vaporizers, isoflurane vaporizers, etc., which cannot be used in common with each other. The vaporizers of modern anesthesia machines are mostly placed outside the anesthesia breathing circuit, and are connected with a separate oxygen flow. The evaporated inhalation anesthetic vapor is mixed with the main air flow before being inhaled by the patient.
OUR EXHIBITION




Good Feetback
Products catalog
Related products
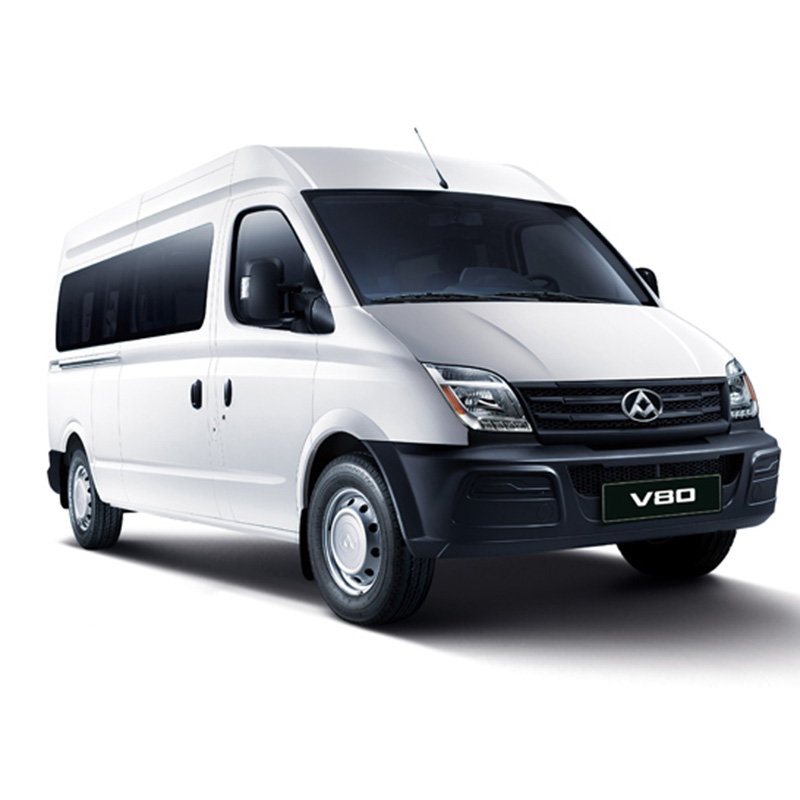
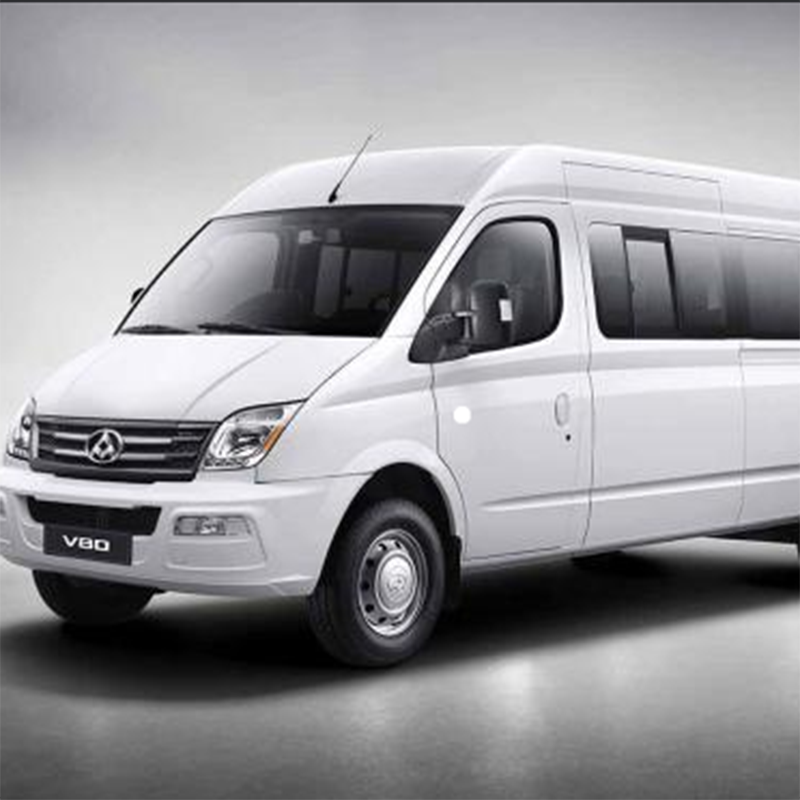


Product detail pictures:
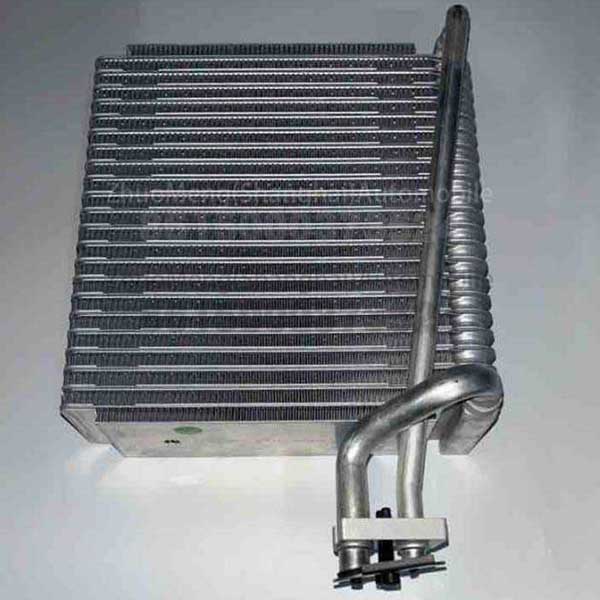



Related Product Guide:
We have been experienced manufacturer. Wining the majority of the crucial certifications of its market for New Fashion Design for Mg3 Spare Parts Wholesale - factory price SAIC MAXUS V80 front evaporator core C00013620 – Zhuomeng , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Sacramento, Mexico, Oman, We have been perfectly devoted to the design, R&D, manufacture, sale and service of hair products during 10 years of development. We have introduced and are making full use of internationally advanced technology and equipment, with advantages of skilled workers. "Dedicated to providing reliable customer service" is our aim. We are sincerely looking forward to establishing business relationships with friends from at home and abroad.
This company conforms to the market requirement and joins in the market competition by its high quality product, this is an enterprise that have Chinese spirit.