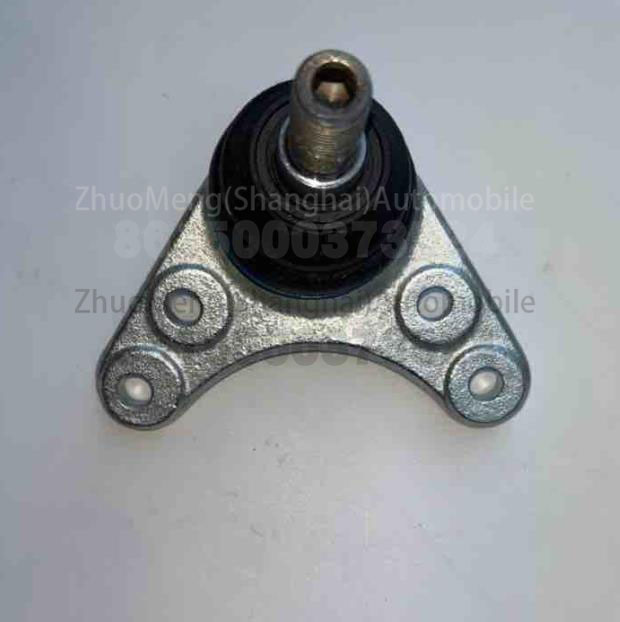
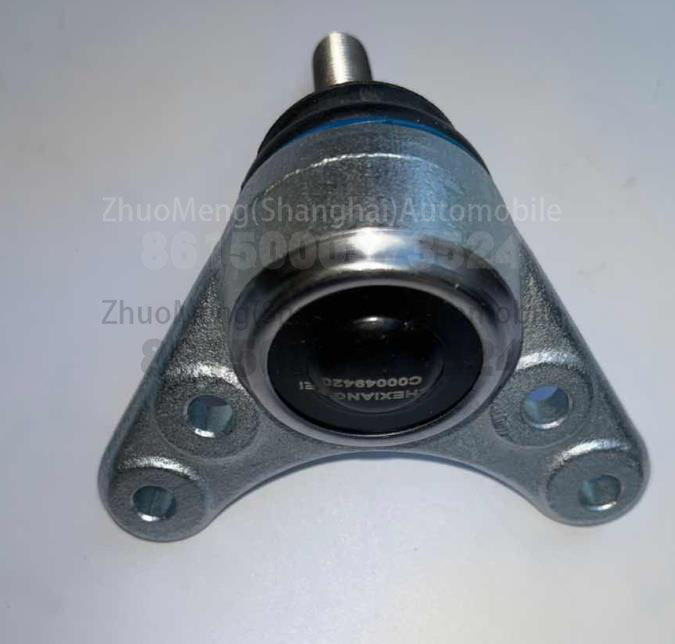
Factory price SAIC MAXUS T60 C00021134 Swing arm ball head
Short Description:
Product Detail
Product Tags
Products information
| Products name | Swing arm ball head |
| Products application | SAIC MAXUS T60 |
| Products OEM NO | C00049420 |
| Org of place | MADE IN CHINA |
| Brand | CSSOT /RMOEM/ORG/COPY |
| Lead time | Stock,if less 20 PCS,normal one month |
| Payment | TT Deposit |
| Company Brand | CSSOT |
| Application system | Chassis system |
Products knowledge
concept
A typical suspension structure is composed of elastic elements, guide mechanisms, shock absorbers, etc., and some structures also have buffer blocks, stabilizer bars, etc. Elastic elements are in the form of leaf springs, air springs, coil springs, and torsion bar springs. Modern car suspensions mostly use coil springs and torsion bar springs, and some high-end cars use air springs.
Part function:
shock absorber
Function: The shock absorber is the main component that generates the damping force. Its function is to quickly attenuate the vibration of the car, improve the ride comfort of the car, and enhance the adhesion between the wheel and the ground. In addition, the shock absorber can reduce the dynamic load of the body part, Extend the service life of the car. The shock absorber widely used in the car is mainly the cylinder type hydraulic shock absorber, and its structure can be divided into three types: double cylinder type, single cylinder inflatable type and double cylinder inflatable type. [2]
Working principle: When the wheel jumps up and down, the piston of the shock absorber reciprocates in the working chamber, so that the liquid of the shock absorber passes through the orifice on the piston, because the liquid has a certain viscosity and when the liquid passes through the orifice, it is in contact with the hole wall Friction is generated between them, so that kinetic energy is converted into heat energy and dissipated into the air, so as to achieve the function of damping vibration.
(2) Elastic elements
Function: support vertical load, ease and restrain vibration and impact caused by uneven road surface. Elastic elements mainly include leaf spring, coil spring, torsion bar spring, air spring and rubber spring, etc.
Principle: Parts made of materials with high elasticity, when the wheel is subjected to a large impact, the kinetic energy is converted into elastic potential energy and stored, and released when the wheel jumps down or returns to the original driving state.
(3) Guide mechanism
The role of the guiding mechanism is to transmit force and moment, and also play a guiding role. During the driving process of the car, the trajectory of the wheels can be controlled.
effect
Suspension is an important assembly in a car, which elastically links the frame with the wheels, and is related to the various performances of the car. From the outside, the car suspension is only composed of some rods, tubes and springs, but don't think it is very simple. On the contrary, the car suspension is a car assembly that is difficult to meet the perfect requirements, because the suspension is both To meet the comfort requirements of the car, it is also necessary to meet the requirements of its handling stability, and these two aspects are opposite to each other. For example, in order to achieve good comfort, it is necessary to greatly cushion the vibration of the car, so the spring should be designed to be softer, but the spring is soft, but it is easy to cause the car to brake "nod", accelerate "head up" and seriously roll left and right. The tendency is not conducive to the steering of the car, and it is easy to cause the car to be unstable.
non-independent suspension
The structural feature of the non-independent suspension is that the wheels on both sides are connected by an integral axle, and the wheels together with the axle are suspended under the frame or vehicle body through elastic suspension. Non-independent suspension has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, high strength, easy maintenance, and small changes in front wheel alignment during driving. However, due to its poor comfort and handling stability, it is basically no longer used in modern cars. , mostly used in trucks and buses.
Leaf spring non-independent suspension
The leaf spring is used as the elastic element of the non-independent suspension. Because it also acts as a guiding mechanism, the suspension system is greatly simplified.
Longitudinal leaf spring non-independent suspension uses leaf springs as elastic elements and is arranged on the car parallel to the longitudinal axis of the car.
Working principle: When the car runs on an uneven road and encounters an impact load, the wheels drive the axle to jump up, and the leaf spring and the lower end of the shock absorber also move up at the same time. The length increase during the upward movement of the leaf spring can be coordinated by the extension of the rear lug without interference. Because the upper end of the shock absorber is fixed and the lower end moves up, it is equivalent to working in a compressed state, and the damping is increased to attenuate the vibration. When the jumping amount of the axle exceeds the distance between the buffer block and the limit block, the buffer block contacts and is compressed with the limit block. [2]
Classification: The longitudinal leaf spring non-independent suspension can be divided into asymmetric longitudinal leaf spring non-independent suspension, balanced suspension and symmetrical longitudinal leaf spring non-independent suspension. It is a non-independent suspension with longitudinal leaf springs.
1. Asymmetric longitudinal leaf spring non-independent suspension
Asymmetric longitudinal leaf spring non-independent suspension refers to a suspension in which the distance between the center of the U-shaped bolt and the center of the lugs at both ends is not equal when the longitudinal leaf spring is fixed to the axle (bridge).
2. Balance suspension
A balanced suspension is a suspension that ensures that the vertical load on the wheels on the connected axle (axle) is always equal. The function of using a balanced suspension is to ensure good contact between the wheels and the ground, the same load, and to ensure that the driver can control the direction of the car and the car has sufficient driving force.
According to different structures, the balance suspension can be divided into two types: thrust rod type and swing arm type.
①Thrust rod balance suspension. It is formed with a vertically placed leaf spring, and its two ends are placed in the slide plate type support on the top of the rear axle axle sleeve. The middle part is fixed on the balance bearing shell through U-shaped bolts, and can rotate around the balance shaft, and the balance shaft is fixed on the vehicle frame through a bracket. One end of the thrust rod is fixed on the vehicle frame, and the other end is connected with the axle. The thrust rod is used to transmit driving force, braking force and corresponding reaction force.
The working principle of the thrust rod balance suspension is a multi-axle vehicle driving on an uneven road. If each wheel adopts a typical steel plate structure as the suspension, it cannot ensure that all the wheels are in full contact with the ground, that is, some wheels bear the vertical A reduced load (or even zero) would make it difficult for the driver to control the direction of travel if it occurs on the steered wheels. If it happens to the drive wheels, some (if not all) of the driving force will be lost. Install the middle axle and the rear axle of the three-axle vehicle on the two ends of the balance bar, and the middle part of the balance bar is hingedly connected with the vehicle frame. Therefore, the wheels on the two bridges cannot move up and down independently. If any wheel sinks in a pit, the other wheel moves upward under the influence of the balance bar. Since the arms of the stabilizer bar are of equal length, the vertical load on both wheels is always equal.
The thrust rod balance suspension is used for the rear axle of the 6×6 three-axle off-road vehicle and the 6×4 three-axle truck.
②Swing arm balance suspension. The mid-axle suspension adopts a longitudinal leaf spring structure. The rear lug is attached to the front end of the swing arm, while the swing arm axle bracket is attached to the frame. The rear end of the swing arm is connected to the rear axle (axle) of the car.
The working principle of the swing arm balance suspension is that the car is driving on an uneven road. If the middle bridge falls into a pit, the swing arm will be pulled down through the rear lug and rotate counterclockwise around the swing arm shaft. The axle wheel will move up. The swing arm here is quite a lever, and the distribution ratio of the vertical load on the middle and rear axles depends on the leverage ratio of the swing arm and the front and rear lengths of the leaf spring.
Coil spring non-independent suspension
Because the coil spring, as an elastic element, can only bear vertical loads, a guiding mechanism and a shock absorber should be added to the suspension system.
It consists of coil springs, shock absorbers, longitudinal thrust rods, lateral thrust rods, reinforcing rods and other components. The structural feature is that the left and right wheels are connected as a whole with a whole shaft. The lower end of the shock absorber is fixed on the rear axle support, and the upper end is hinged with the vehicle body. The coil spring is set between the upper spring and the lower seat on the outside of the shock absorber. The rear end of the longitudinal thrust rod is welded on the axle and the front end is hinged to the vehicle frame. One end of the transverse thrust rod is hinged on the vehicle body, and the other end is hinged on the axle. When working, the spring bears the vertical load, and the longitudinal force and transverse force are respectively borne by the longitudinal and transverse thrust rods. When the wheel jumps, the entire axle swings around the hinge points of the longitudinal thrust rod and the lateral thrust rod on the vehicle body. Rubber bushings at the articulation points eliminate motion interference when the axle swings. The coil spring non-independent suspension is suitable for the rear suspension of passenger cars.
Air spring non-independent suspension
When the car is running, due to the change of the load and the road surface, the stiffness of the suspension is required to change accordingly. Cars are required to reduce the height of the body and increase the speed on good roads; to increase the height of the body and increase the passing capacity on bad roads, so the height of the body is required to be adjustable according to the use requirements. Air spring non-independent suspension can meet such requirements.
It is composed of compressor, air storage tank, height control valve, air spring, control rod, etc. In addition, there are shock absorbers, guide arms, and lateral stabilizer bars. The air spring is fixed between the frame (body) and the axle, and the height control valve is fixed on the vehicle body. The end of the piston rod is hinged with the cross arm of the control rod, and the other end of the cross arm is hinged with the control rod. The middle part is supported on the upper part of the air spring, and the lower end of the control rod is fixed on the axle. The components that make up the air spring are connected together through pipelines. The high-pressure gas generated by the compressor enters the air storage tank through the oil-water separator and pressure regulator, and then enters the height control valve through the air filter after coming out of the gas storage tank. The air storage tank, the air storage tank is connected with the air springs on each wheel, so the gas pressure in each air spring increases with the increase of the inflated amount, and at the same time, the body is lifted until the piston in the height control valve will move toward the air storage tank The air filling port of the inner inflation is blocked. As an elastic element, the air spring can alleviate the impact load acting on the wheel from the road surface when it is transmitted to the vehicle body through the axle. In addition, the air suspension can also automatically adjust the height of the vehicle body. The piston is located between the inflation port and the air discharge port in the height control valve, and the gas from the air storage tank inflates the air storage tank and the air spring, and raises the height of the vehicle body. When the piston is in the upper position of the inflation port in the height control valve, the gas in the air spring returns to the air discharge port through the inflation port and enters the atmosphere, and the air pressure in the air spring drops, so the height of the vehicle body also drops. The control rod and the cross arm on it determine the position of the piston in the height control valve.
The air suspension has a series of advantages such as making the car drive with good ride comfort, realizing single-axis or multi-axis lifting when necessary, changing the height of the vehicle body and causing little damage to the road surface, etc., but it also has a complex structure and strict requirements for sealing. and other shortcomings. It is used in commercial passenger cars, trucks, trailers and some passenger cars.
Oil and gas spring non-independent suspension
The oil-pneumatic spring non-independent suspension refers to the non-independent suspension when the elastic element adopts oil-pneumatic spring.
It is composed of oil and gas springs, lateral thrust rods, buffer blocks, longitudinal thrust rods and other components. The upper end of the oil-pneumatic spring is fixed on the vehicle frame, and the lower end is fixed on the front axle. The left and right sides respectively use a lower longitudinal thrust rod to be contained between the front axle and the longitudinal beam. An upper longitudinal thrust rod is mounted on the front axle and the inner bracket of the longitudinal beam. The upper and lower longitudinal thrust rods form a parallelogram, which is used to ensure that the caster angle of the kingpin remains unchanged when the wheel jumps up and down. The transverse thrust rod is mounted on the left longitudinal beam and the bracket on the right side of the front axle. A buffer block is installed under the two longitudinal beams. Because the oil-pneumatic spring is installed between the frame and the axle, as an elastic element, it can ease the impact force from the road surface on the wheel when it is transmitted to the frame, and at the same time attenuate the ensuing vibration. The upper and lower longitudinal thrust rods are used to transmit the longitudinal force and withstand the reaction moment caused by the braking force. Lateral thrust rods transmit lateral forces.
When the oil-gas spring is used on a commercial truck with a large load, its volume and mass are smaller than that of the leaf spring and it has variable stiffness characteristics, but it has high requirements for sealing and difficult maintenance. The oil-pneumatic suspension is suitable for commercial trucks with heavy loads.
Independent Suspension Editorial Broadcast
Independent suspension means that the wheels on each side are individually suspended from the frame or body by elastic suspensions. Its advantages are: light weight, reducing the impact on the body, and improving the ground adhesion of the wheels; soft springs with small stiffness can be used to improve the comfort of the car; the position of the engine can be lowered, and the center of gravity of the car can also be lowered, thereby Improve the driving stability of the car; the left and right wheels jump independently and are independent of each other, which can reduce the tilt and vibration of the car body. However, the independent suspension has the disadvantages of complex structure, high cost and inconvenient maintenance. Most modern cars use independent suspensions. According to different structural forms, independent suspensions can be divided into wishbone suspensions, trailing arm suspensions, multi-link suspensions, candle suspensions, and MacPherson suspensions.
wishbone
Cross-arm suspension refers to the independent suspension in which wheels swing in the transverse plane of the automobile. It is divided into double-arm suspension and single-arm suspension according to the number of cross-arms.
The single wishbone type has the advantages of simple structure, high roll center and strong anti-roll capability. However, with the increase of the speed of modern cars, the excessively high roll center will cause a large change in the wheel track when the wheels jump, and the tire wear will increase. Moreover, the vertical force transfer of the left and right wheels will be too large during sharp turns, resulting in increased camber of the rear wheels. The cornering stiffness of the rear wheel is reduced, resulting in severe conditions of high-speed tail drift. The single-wishbone independent suspension is mostly used in the rear suspension, but because it cannot meet the requirements of high-speed driving, it is not used much at present.
Double-wishbone independent suspension is divided into equal-length double-wishbone suspension and unequal-length double-wishbone suspension according to whether the upper and lower cross-arms are equal in length. The equal-length double-wishbone suspension can keep the kingpin inclination constant when the wheel jumps up and down, but the wheelbase changes greatly (similar to the single-wishbone suspension), which causes serious tire wear and tear, and is rarely used now. For the unequal-length double-wishbone suspension, as long as the length of the upper and lower wishbone is properly selected and optimized, and through reasonable arrangement, the changes of the wheelbase and front wheel alignment parameters can be kept within acceptable limits, ensuring that the vehicle Has good driving stability. At present, the unequal-length double-wishbone suspension has been widely used in the front and rear suspensions of cars, and the rear wheels of some sports cars and racing cars also use this suspension structure.
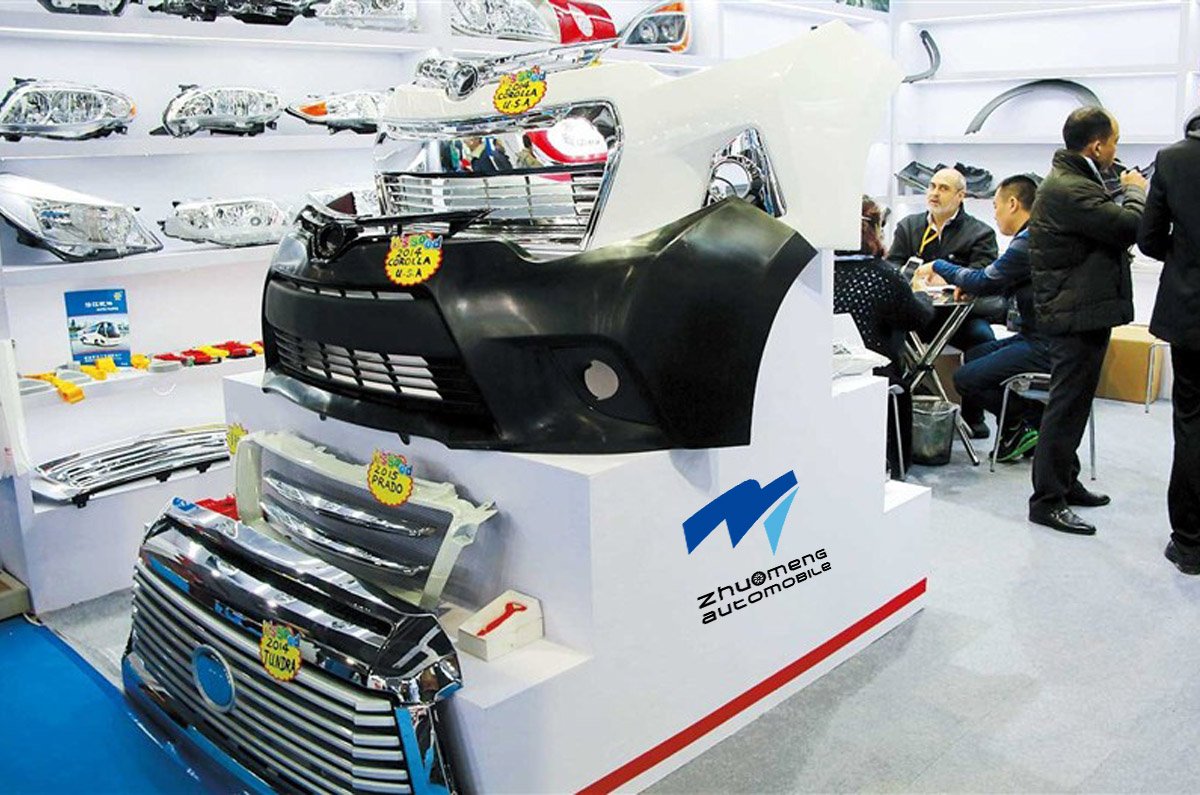
OUR EXHIBITION




Good Feetback


Related products









